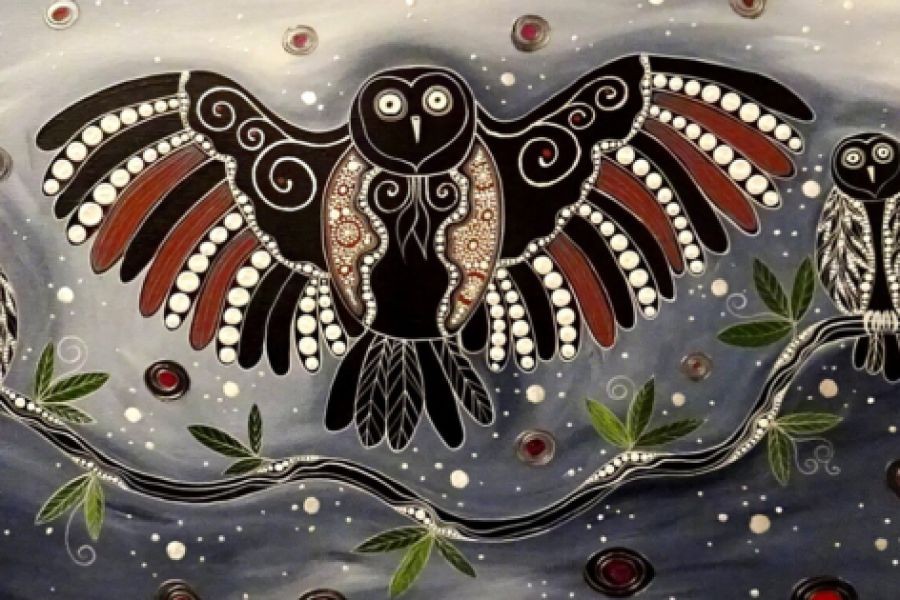
Australia's Indigenous art scene is experiencing a remarkable resurgence, characterized by a renewed focus on cultural heritage and creative innovation. This revival is not just an artistic endeavor but also a significant economic and cultural phenomenon. As the demand for Indigenous art grows both locally and internationally, the implications for Australia's economy and industries are profound. This article delves into the factors driving this resurgence, its economic impact, and the broader cultural significance.
The Economic Impact of Indigenous Art
The Indigenous art market in Australia is experiencing substantial growth, contributing significantly to the national economy. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, the arts and culture sector, including Indigenous art, contributes approximately AUD 111.7 billion to the Australian economy annually. This figure highlights the economic potential of Indigenous art as a key driver of growth and employment, particularly in remote communities where many Indigenous artists reside.
Global Demand and Local Impact
International interest in Indigenous art has surged, with collectors and galleries worldwide seeking authentic pieces. This demand not only benefits Australian artists but also boosts the country's cultural exports. The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) indicates that cultural exports, including art, have seen a 15% increase in the past five years. This growth underscores the potential for Indigenous art to enhance Australia's trade balance and international cultural standing.
Case Study: The Rise of Indigenous Art Collectives
One notable example of the Indigenous art resurgence is the success of art collectives such as the Tjala Arts in South Australia. This collective has seen a dramatic increase in international recognition and sales. By fostering collaboration among artists, these collectives have been able to negotiate better terms for their work, ensuring fair compensation and sustainable practices.
Problem: Indigenous artists often faced exploitation, with their works undervalued in global markets.
Action: Tjala Arts implemented a cooperative model, empowering artists to control pricing and distribution.
Result: The collective achieved a 30% increase in sales and expanded its market reach internationally, setting a benchmark for ethical art trade.
Takeaway: Indigenous art collectives can enhance economic empowerment and cultural preservation, offering a model for sustainable growth.
The Role of Technology in Indigenous Art
Technology is playing a pivotal role in the resurgence of Indigenous art. Artists are leveraging digital platforms to reach wider audiences, transcending geographical barriers. Online marketplaces and social media have become vital tools for promoting and selling art, allowing artists to connect directly with buyers. This direct engagement is crucial for maintaining the authenticity of the art and ensuring that artists receive fair compensation.
Moreover, digital tools allow Indigenous artists to experiment with new forms and techniques, blending traditional motifs with modern aesthetics. This fusion not only attracts younger audiences but also preserves cultural narratives in innovative ways.
Regulatory Insights and Fair Trade
The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) plays a critical role in ensuring fair trade practices in the Indigenous art market. Recent regulations have been introduced to combat the proliferation of fake Indigenous art, which undermines the value and integrity of authentic works. The ACCC's guidelines aim to protect artists' rights and ensure that consumers receive genuine pieces, bolstering confidence in the market.
Pros and Cons of the Indigenous Art Resurgence
Pros:
- Economic Growth: Indigenous art significantly contributes to Australia's GDP and employment, especially in remote communities.
- Cultural Preservation: The art resurgence helps preserve and promote Indigenous cultural heritage.
- Global Recognition: Australia gains international acclaim for its rich cultural diversity and artistic contributions.
- Innovation: Artists are blending traditional and contemporary techniques, attracting diverse audiences.
Cons:
- Exploitation Risks: Without proper regulation, artists may face exploitation in global markets.
- Authenticity Concerns: The rise of counterfeit art products can damage the market's credibility.
- Market Volatility: As with any art market, values can fluctuate, posing risks to investors and artists alike.
Future Trends in Indigenous Art
The future of Indigenous art in Australia looks promising, driven by both technological advancements and increasing global interest. According to a report by Deloitte, the Indigenous art market is expected to grow by 20% over the next five years. This growth will likely be fueled by the expansion of digital platforms and continued efforts to protect and promote authentic Indigenous art.
Furthermore, educational programs and cultural exchanges will play a vital role in sustaining this growth. By fostering a deeper understanding of Indigenous cultures and histories, these initiatives will contribute to the appreciation and demand for Indigenous art globally.
Common Myths About Indigenous Art
Myth: Indigenous art is only traditional and lacks modern relevance. Reality: Indigenous artists are blending traditional and contemporary styles, making their work relevant and appealing to modern audiences.
Myth: All Indigenous art is expensive and inaccessible. Reality: While some pieces are high-value, there is a wide range of art available at various price points, making it accessible for diverse collectors.
Myth: Indigenous art lacks global appeal. Reality: The increasing demand and international exhibitions demonstrate the global appeal and significance of Indigenous art.
Conclusion
The resurgence of Indigenous art in Australia is more than just an artistic trend; it is a significant cultural and economic movement with far-reaching implications. By embracing technology, fostering ethical practices, and promoting cultural education, Australia can ensure that Indigenous art continues to thrive both locally and globally. As this market evolves, it offers not only economic opportunities but also a chance to celebrate and preserve the rich cultural heritage of Australia's Indigenous peoples.
Final Takeaways
- The Indigenous art market is a growing economic force in Australia, contributing significantly to GDP.
- Technological advancements are transforming how Indigenous art is created, shared, and sold.
- Regulatory measures are crucial in maintaining the integrity and authenticity of the market.
- Future growth will be driven by digital platforms and international collaborations.
People Also Ask
How does Indigenous art impact Australia's economy? Indigenous art contributes significantly to Australia's GDP, with the arts and culture sector adding approximately AUD 111.7 billion annually.
What are the biggest misconceptions about Indigenous art? One common myth is that Indigenous art is only traditional. In reality, artists blend traditional and modern styles, appealing to diverse audiences.
What are the best strategies for promoting Indigenous art? Experts recommend leveraging digital platforms, ensuring fair trade practices, and fostering international collaborations for long-term success.
Related Search Queries
- Indigenous art market growth Australia
- Impact of technology on Indigenous art
- Authenticity in Indigenous art
- Indigenous art collectives in Australia
- Future trends in Indigenous art
- Global demand for Australian Indigenous art
- Regulations in the Indigenous art market
- Economic impact of Indigenous art in Australia































ONZHumbert
9 months ago