Telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in the healthcare industry, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance patient care. With New Zealand's unique healthcare challenges, such as geographic isolation and a dispersed population, telemedicine presents a valuable solution for improving access and quality of care. This article delves into the mechanisms of telemedicine, its impact on patient care, and its potential in New Zealand's healthcare landscape.
How Telemedicine Works: A Deep Dive
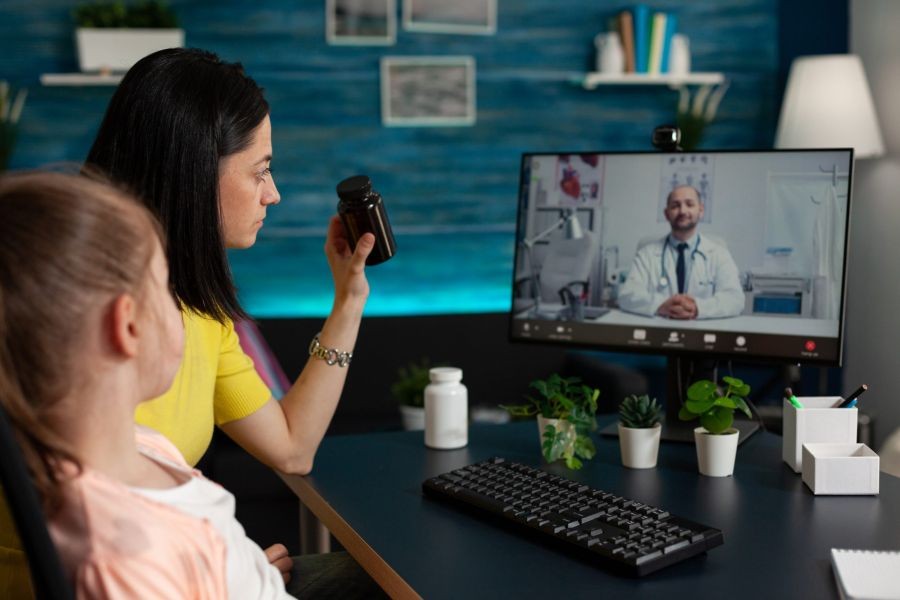
Telemedicine utilizes digital communication technologies to provide healthcare services remotely. It encompasses a range of applications, from video consultations and remote monitoring to mobile health apps and electronic health records. By leveraging these technologies, healthcare providers can offer timely diagnosis and treatment, thereby enhancing patient outcomes and satisfaction.
In New Zealand, the Ministry of Health has recognized telemedicine's potential, especially in reaching rural communities. According to a report by the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (MBIE), telemedicine could reduce healthcare costs by up to 20% by decreasing unnecessary hospital visits and enabling efficient resource allocation.
Expert Opinions & Thought Leadership
Dr. Emily Thompson, a leading telemedicine advocate in New Zealand, emphasizes the critical role of telemedicine in addressing healthcare disparities. "By connecting patients with specialists across the country, we can ensure that everyone receives the care they need, regardless of their location," she states. Her insights are backed by a study from the University of Auckland, which found that telemedicine consultations have increased patient engagement by 30% compared to traditional methods.
Real-World Case Study: Telemedicine Success in Rural New Zealand
Case Study: Rural Health Clinic – Enhancing Access to Specialist Care
Problem: A rural health clinic in the South Island struggled with providing specialist care due to geographical barriers and limited resources. Patients often faced long travel distances and waiting times, leading to delayed diagnoses and treatments.
Action: The clinic implemented a telemedicine program, enabling virtual consultations with specialists from urban centers. They used secure video conferencing tools and integrated electronic health records to streamline the process.
Result: Within a year, the clinic reported significant improvements: ✅ Specialist consultation wait times decreased by 40%. ✅ Patient satisfaction scores improved by 25%. ✅ The clinic saved approximately NZD 100,000 in transportation and operation costs.
Takeaway: This case study highlights telemedicine's capacity to bridge healthcare gaps in rural areas. New Zealand clinics can adopt similar strategies to enhance access and reduce costs, aligning with the government's goals of equitable healthcare for all.
Pros vs. Cons of Telemedicine
While telemedicine offers numerous benefits, it's essential to weigh its advantages against potential drawbacks.
✅ Pros:
- Increased Accessibility: Patients in remote areas can access specialist care without traveling long distances.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces travel expenses and hospital admissions, leading to significant savings.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Convenient access encourages patients to seek timely treatment and follow-up care.
- Scalability: Suitable for diverse healthcare settings, from small clinics to large hospitals.
❌ Cons:
- Technological Barriers: Requires reliable internet connectivity and access to digital devices, which may be challenging for some populations.
- Privacy Concerns: Ensuring data security and patient confidentiality is critical.
- Regulatory Challenges: Compliance with healthcare regulations can be complex, particularly in cross-border consultations.
Common Myths & Mistakes in Telemedicine
Despite its benefits, telemedicine is often surrounded by misconceptions that can hinder its adoption.
Myth: "Telemedicine offers inferior care compared to in-person visits." Reality: Studies show that telemedicine consultations are as effective as in-person visits for many conditions, providing timely and accurate diagnoses.
Myth: "Telemedicine is only for tech-savvy patients." Reality: User-friendly platforms and support services ensure that patients of all ages and technological skills can benefit from telemedicine.
Myth: "Telemedicine is too costly for clinics to implement." Reality: While initial setup costs exist, telemedicine can lead to substantial long-term savings through reduced operational expenses and increased patient volumes.
Future Trends & Predictions in Telemedicine
The future of telemedicine in New Zealand looks promising, with several trends poised to shape its trajectory. According to a report by NZTech, the telemedicine market is expected to grow by 15% annually, driven by advancements in AI and machine learning. These technologies will enhance diagnostic accuracy and personalize patient care, making telemedicine an integral component of the healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion: Enhancing Patient Care Through Telemedicine
Telemedicine offers a powerful tool for improving patient care in New Zealand, addressing geographic and resource challenges while enhancing accessibility and satisfaction. By overcoming technological barriers and regulatory hurdles, telemedicine can revolutionize the healthcare landscape, ensuring equitable and efficient care for all Kiwis.
Ready to explore the potential of telemedicine in your practice? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and join the conversation on transforming healthcare in New Zealand.
People Also Ask (FAQ)
How does telemedicine impact healthcare in New Zealand? Telemedicine enhances accessibility and reduces costs, particularly in rural areas. According to MBIE, it can decrease healthcare expenses by up to 20%.
What are the biggest misconceptions about telemedicine? One common myth is that telemedicine offers inferior care. However, studies show it is as effective as in-person visits for many conditions.
What strategies are best for implementing telemedicine? Experts recommend starting with secure video conferencing tools, integrating electronic health records, and ensuring data privacy for successful implementation.
Related Search Queries
- Telemedicine in New Zealand
- Benefits of telemedicine
- Telemedicine case studies
- Telemedicine vs. traditional healthcare
- Future of telemedicine
- Telemedicine myths
- Implementing telemedicine in clinics
- Telemedicine challenges
- Telemedicine privacy concerns
- Telemedicine technology requirements






























Hot Flush Plumbing
7 months ago