Australia's export restrictions, often viewed through an economic lens, are deeply intertwined with political tensions that influence the global mining and resources landscape. As the world's largest exporter of iron ore and a significant player in coal, gold, and natural gas markets, Australia's policies hold considerable sway. But beneath these economic strategies lie complex political dynamics that shape, and are shaped by, international relations and domestic policies.
Understanding Australia's Export Landscape
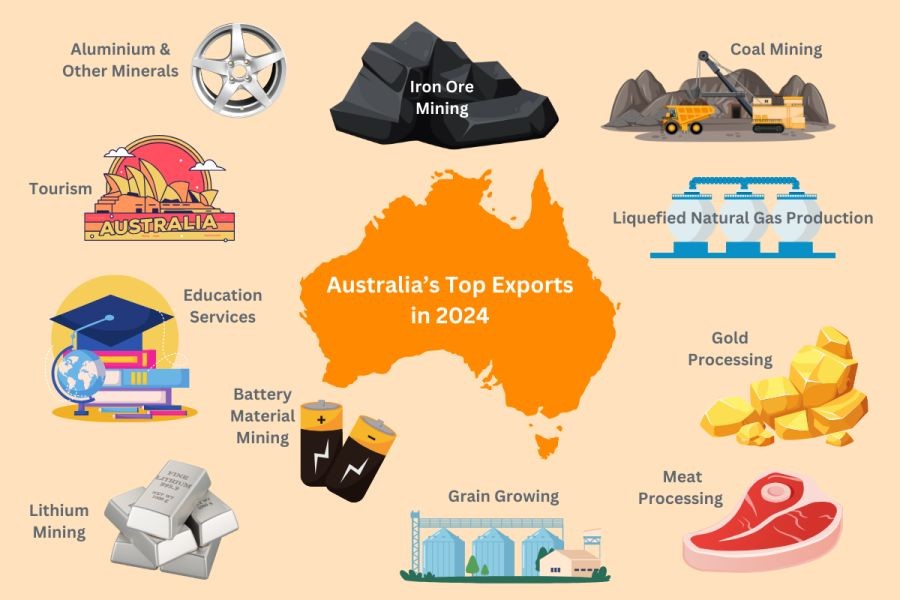
Australia's economy relies heavily on its vast natural resources. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, mining constituted approximately 10% of the country's GDP in 2022, highlighting its critical role in national prosperity. However, recent export restrictions have sparked debates over their political motivations and implications.
Political Influences on Export Decisions
Australia's export policies are not solely driven by economic goals. Political considerations, such as national security, environmental concerns, and international relations, significantly influence these decisions. For instance, the strategic partnership with the United States and tensions with China have led to a reassessment of export strategies, particularly concerning critical minerals like lithium and rare earth elements.
Case Study: The China Factor in Export Restrictions
The political tension between Australia and China over the past decade provides a clear example of how geopolitics can impact export policies. In 2020, China imposed tariffs on Australian barley and restricted coal imports following diplomatic disagreements. This move forced Australia to diversify its export markets, highlighting the interconnectedness of politics and trade.
- Problem: Australia faced reduced coal exports to China, its largest market, leading to significant revenue losses.
- Action: Australia sought new markets in India and Southeast Asia, leveraging its vast reserves to negotiate favorable terms.
- Result: By 2022, Australia had successfully increased its coal exports to India by 30%, partially offsetting losses from the Chinese market.
- Takeaway: Diversifying export markets can mitigate geopolitical risks, though it requires strategic foresight and adaptability.
Economic Implications of Export Restrictions
While political motivations play a significant role, the economic implications of export restrictions cannot be overlooked. The Reserve Bank of Australia reports that export revenues from the mining sector are projected to decline by 5% in 2023 due to ongoing restrictions and market volatility. This decline could pressure the Australian dollar and impact national economic growth.
Pros and Cons of Export Restrictions
✅ Pros:
- National Security: Ensures critical minerals are available for domestic industries.
- Environmental Protection: Reduces environmental degradation by limiting over-extraction.
- Market Stability: Protects local industries from volatile global market changes.
❌ Cons:
- Economic Loss: Reduced export revenues can strain national budgets.
- Global Relations: May lead to trade disputes and diplomatic tensions.
- Market Diversification Challenges: Finding new markets can be time-consuming and costly.
Future Trends and Predictions
The future of Australia's export restrictions is likely to be shaped by emerging global trends. A Deloitte report predicts that by 2028, global demand for critical minerals will double, driven by advancements in technology and renewable energy. Australia, with its rich deposits, stands to benefit, provided it navigates the geopolitical landscape effectively.
Moreover, the push for net-zero emissions by 2050 will necessitate a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability. Australia's export strategies will need to align with global climate goals, influencing its political and economic policies.
Common Myths and Mistakes
Several misconceptions surround Australia's export restrictions:
- Myth: Export restrictions are purely economic decisions.
- Reality: Political and environmental factors play significant roles, often more influential than economic considerations.
- Myth: Australia's export market is inflexible.
- Reality: Despite challenges, Australia has successfully diversified its markets, particularly in Asia.
- Myth: Export restrictions harm local industries.
- Reality: While they can pose challenges, they also protect local industries from global market volatility.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future
Australia's export restrictions are a complex interplay of political, economic, and environmental factors. Understanding these hidden tensions is crucial for mining and resource strategists aiming to navigate the global market effectively. As Australia looks to the future, balancing these elements will be key to maintaining its position as a leading exporter while ensuring national prosperity and security.
What's your take on Australia's export strategies? Share your insights and experiences below!
People Also Ask (FAQ)
- How do Australia's export restrictions impact its economy? Export restrictions can lead to reduced revenue, affecting national economic growth. However, they also protect critical industries and resources.
- What are the political motivations behind these restrictions? Political motivations include national security, international relations, and environmental protection, influencing Australia's export policies.
- How can businesses adapt to these restrictions? Businesses can adapt by diversifying markets, investing in sustainable practices, and staying informed on geopolitical developments.
Related Search Queries
- Australia export restrictions 2023
- Impact of geopolitical tensions on Australian mining
- Australia-China trade relations
- Future of Australia's mining exports
- Environmental impact of mining in Australia





























FredOnslow
11 months ago