The rise of cyber threats globally necessitates a paradigm shift in how nations approach cybersecurity. As Australia navigates the complexities of digital transformation, the question looms: will it ever adopt a ‘Zero Trust’ national cybersecurity model? This model, emphasizing the principle of 'never trust, always verify,' could redefine the country's approach to securing its digital landscape. Let's delve into the intricacies of this model and explore its potential implications for Australia’s economy, industries, and policies.
Understanding the Zero Trust Model
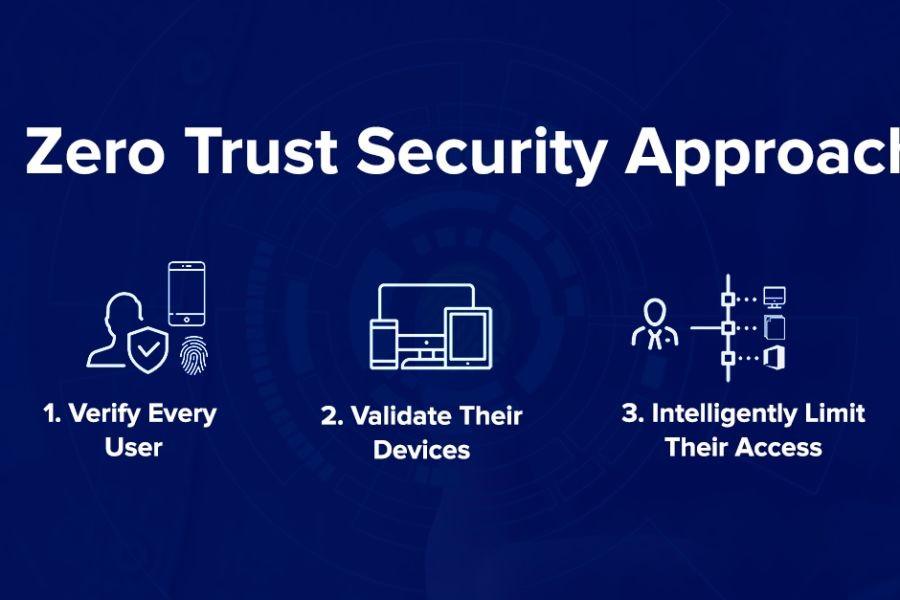
The Zero Trust model is a cybersecurity framework that assumes threats may exist both outside and inside a network. Unlike traditional models that rely on perimeter security, Zero Trust requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources on a private network. This approach mitigates the risks of data breaches by ensuring that even if a network is compromised, the damage can be contained.
Why Zero Trust Matters for Australia
Australia's digital economy is rapidly growing, with the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) noting a significant increase in the digital economy's contribution to the GDP. As digital infrastructures expand, so do vulnerabilities. A Zero Trust approach could safeguard critical sectors such as finance, healthcare, and superannuation by providing a robust defense mechanism against sophisticated cyber threats.
Risk & Threat Assessment
Cyber threats have become more sophisticated, targeting critical infrastructure and sensitive data. According to the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC), the country experienced a 13% increase in cybercrime reports in 2022, underscoring the urgency for more secure frameworks. The Zero Trust model's ability to limit unauthorized access makes it a formidable tool against these escalating threats.
Case Study: Implementing Zero Trust in the Financial Sector
Problem: An Australian bank faced repeated phishing attacks, compromising sensitive customer data and leading to financial losses.
Action: The bank adopted a Zero Trust model, implementing strict identity verification protocols and micro-segmentation of its network.
Result: Within a year, the bank reported a 40% reduction in security incidents and improved customer trust.
Takeaway: Zero Trust’s proactive security measures can significantly enhance the resilience of financial institutions against cyber threats.
Government Policy Analysis
The Australian government has been proactive in strengthening the nation's cybersecurity infrastructure through various initiatives and policies. The Cyber Security Strategy 2020 outlines a $1.67 billion investment over ten years to enhance the country's cyber defenses. However, adopting a Zero Trust model at a national level would require significant policy shifts and investments in technology and workforce training.
Regulatory Insights: APRA's Role
The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) plays a crucial role in monitoring the financial sector's cybersecurity posture. By integrating Zero Trust principles into regulatory frameworks, APRA can ensure that financial institutions adhere to the highest security standards, protecting consumers and maintaining market stability.
Real-World Example: Global Zero Trust Adoption
In the United States, the Department of Defense has successfully implemented Zero Trust principles across its networks, significantly reducing data breaches. Australia's adoption of similar strategies could bolster its national cybersecurity, protecting critical infrastructures and maintaining economic stability.
Pros and Cons of Zero Trust Implementation
Pros
- Enhanced Security: By continuously verifying identities, Zero Trust minimizes the risk of unauthorized access.
- Scalability: The model can be applied across various industries, from finance to healthcare.
- Compliance: Supports compliance with stringent data protection regulations.
- Resilience: Limits the impact of breaches by segmenting networks.
Cons
- Implementation Costs: Initial investment in technology and training can be substantial.
- Complexity: Requires comprehensive network restructuring and continuous monitoring.
- Potential for User Frustration: Increased verification processes can lead to user inconvenience.
Common Myths & Mistakes
- Myth: Zero Trust is only for large corporations.Reality: Small and medium enterprises can benefit significantly from Zero Trust, as it provides scalable security solutions tailored to their needs.
- Myth: Implementing Zero Trust is too expensive.Reality: While there are upfront costs, the long-term savings from preventing data breaches often justify the investment.
- Myth: Zero Trust eliminates all risks.Reality: While it significantly reduces risks, no model can provide absolute security.
Future Trends & Predictions
As cyber threats evolve, the demand for Zero Trust security frameworks will likely increase. By 2028, it is predicted that 60% of Australian enterprises will adopt Zero Trust principles (Source: Deloitte Cyber Security Report 2024). This shift could lead to enhanced national security and position Australia as a leader in global cybersecurity practices.
Conclusion
The potential adoption of a Zero Trust model in Australia represents a significant step forward in national cybersecurity. By addressing the unique challenges posed by the digital age, Zero Trust offers a robust framework for protecting Australia’s critical infrastructures. As the nation continues to invest in cybersecurity, the integration of Zero Trust principles could ensure a secure and resilient digital future.
Final Takeaways
- Fact: Zero Trust can significantly reduce cybersecurity risks by verifying all network activities.
- Strategy: Implementing Zero Trust in sectors like finance and healthcare can protect sensitive data and enhance customer trust.
- Mistake to Avoid: Underestimating the complexity and costs of transitioning to a Zero Trust model.
- Pro Tip: Start with a pilot program to identify potential challenges and tailor solutions accordingly.
Call to Action
As Australia faces increasing cyber threats, the adoption of a Zero Trust model may become imperative. Businesses and policymakers must collaborate to drive this transition and ensure a secure digital future. Join the conversation: how do you think Zero Trust could transform Australia's cybersecurity landscape? Share your thoughts below!
People Also Ask
- How does Zero Trust benefit Australian businesses?By adopting Zero Trust, Australian businesses can reduce cyber risks, enhance data protection, and build customer trust, leading to better business outcomes.
- What are the biggest misconceptions about Zero Trust?One common myth is that Zero Trust is only for large corporations. However, it is scalable and beneficial for businesses of all sizes.
- What are the best strategies for implementing Zero Trust?Experts recommend starting with a network assessment, followed by implementing identity verification protocols and continuous monitoring.
Related Search Queries
- Zero Trust cybersecurity Australia
- Benefits of Zero Trust model
- Zero Trust implementation challenges
- Australia cybersecurity strategy 2024
- APRA cybersecurity guidelines
- Cyber threats in Australia 2024
- Zero Trust vs. traditional security models
- Future of cybersecurity in Australia
- Zero Trust for small businesses
- Zero Trust compliance requirements






























BrigidaCar
9 months ago