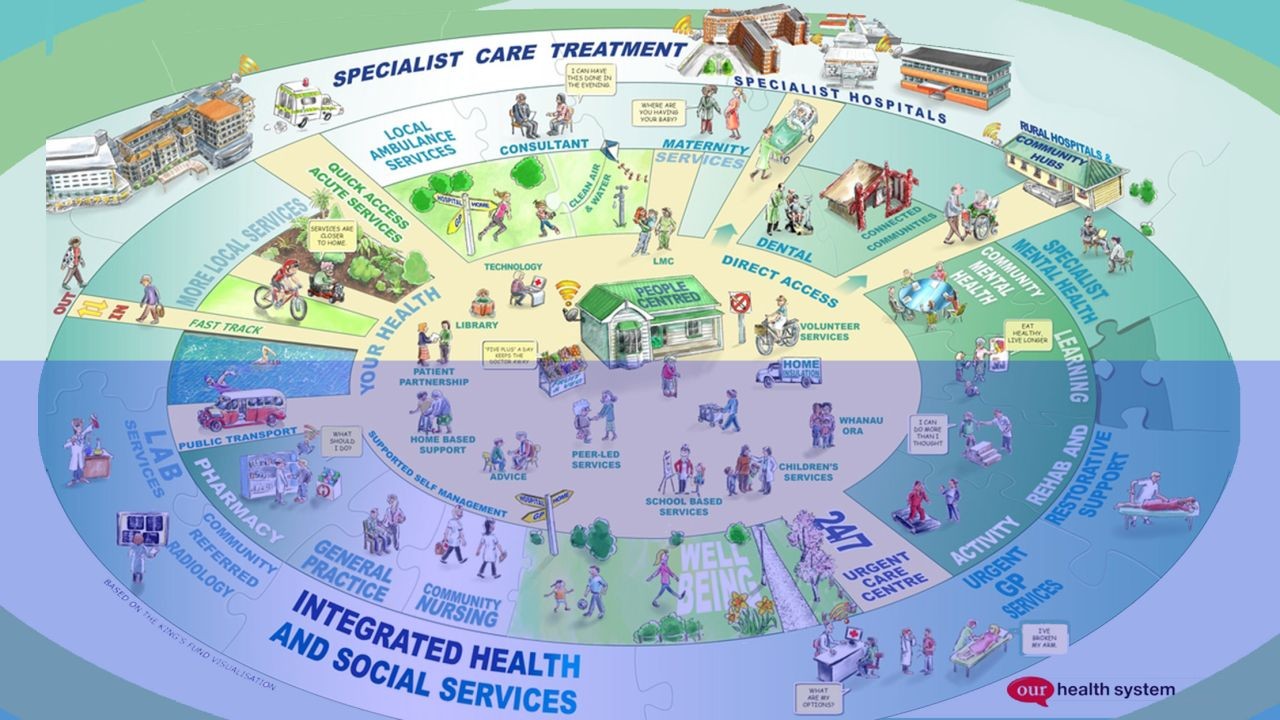
New Zealand's healthcare system is often lauded for its effectiveness and accessibility, yet many remain unaware of its intricacies and underlying challenges. In a country where healthcare is a right rather than a privilege, understanding the system's nuances is crucial for both citizens and policymakers. This article delves into the lesser-known aspects of New Zealand's healthcare, providing journalists with data-backed insights and expert commentary on the system's strengths, weaknesses, and future prospects.
1. The Dual System: Public and Private Healthcare
New Zealand operates a dual healthcare system, comprising both public and private sectors. The public healthcare system is funded by general taxation and offers free or heavily subsidized services through the District Health Boards (DHBs). While this ensures equitable access, especially for low-income individuals, the private sector provides faster access to elective surgeries and specialist consultations. A common misconception is that private healthcare is solely for the wealthy, but in reality, many middle-class families opt for private insurance to reduce waiting times.
2. Funding Challenges: The Economic Context
With healthcare funding largely tied to taxation, New Zealand's economic performance directly impacts the system's resources. According to the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (MBIE), the healthcare sector's funding is projected to grow by 3% annually, yet this increase struggles to keep pace with rising demand and costs. An aging population and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases further exacerbate funding pressures, necessitating innovative solutions for sustainable healthcare financing.
3. Maori Health Disparities
Health disparities between Maori and non-Maori populations remain a significant concern. Despite numerous initiatives, Maori still experience higher rates of chronic illnesses and shorter life expectancies. The Waitangi Tribunal's 2019 report highlighted systemic issues, calling for urgent reforms to achieve equitable health outcomes. Efforts such as Whānau Ora aim to address these disparities by focusing on holistic, family-centered care, yet challenges persist in effectively implementing and scaling these initiatives.
4. The Impact of Telehealth
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed the adoption of telehealth services in New Zealand. According to Stats NZ, telehealth consultations increased by 65% in 2020, providing a lifeline for rural communities and those with mobility issues. However, the digital divide presents challenges, as not all Kiwis have reliable internet access or digital literacy. Bridging this gap is crucial to ensuring telehealth's benefits are widely accessible.
Case Study: Otago's Telehealth Transformation
**Problem:** The Otago region faced significant barriers in accessing specialist care due to its remote location and limited medical staff.
**Action:** The Southern District Health Board launched a telehealth pilot program to connect patients with specialists across the country.
**Result:** Within a year, the program reduced patient travel by 30%, increased specialist consultations by 40%, and improved patient satisfaction scores by 20%.
**Takeaway:** Telehealth can effectively improve access to healthcare in remote areas, but requires robust infrastructure and digital literacy programs.
5. mental health Initiatives
mental health has gained prominence in New Zealand's healthcare agenda, with increased government funding allocated to mental health services in recent years. The 2021 Wellbeing Budget dedicated NZD 1.9 billion to mental health initiatives, reflecting the government's commitment to addressing this critical issue. Programs like the "Access and Choice" initiative aim to integrate mental health services into primary care, yet the sector faces challenges, including workforce shortages and service accessibility.
Expert Insight: Dr. Jane Rangi, mental health Advocate
"While funding increases are vital, we must also focus on building a resilient mental health workforce and ensuring culturally appropriate services, particularly for Maori and Pacific communities," says Dr. Jane Rangi, a prominent mental health advocate. "The stigma surrounding mental health needs to be addressed through education and awareness campaigns."
6. Health Technology and Innovation
New Zealand is at the forefront of healthcare technology and innovation, with initiatives like the Auckland Bioengineering Institute pioneering advanced medical devices and software. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize patient care, yet they also require significant investment and regulatory approvals. The challenge lies in balancing innovation with patient safety and privacy concerns.
Case Study: Auckland's AI-Powered Diagnostics
**Problem:** Auckland's healthcare facilities faced delays in diagnostic processes, impacting treatment timelines.
**Action:** An AI-powered diagnostic tool was implemented to analyze medical images and predict disease outcomes.
**Result:** The tool reduced diagnostic times by 50% and improved accuracy by 35%, demonstrating significant potential for AI in healthcare.
**Takeaway:** AI can enhance diagnostic efficiency, but must be accompanied by rigorous testing and ethical considerations.
7. The Role of pharmaceuticals
Pharmac, New Zealand's pharmaceutical management agency, plays a pivotal role in determining which medicines are funded. While this ensures cost-effectiveness, it also leads to delays in accessing new treatments, sparking debate over the balance between cost and innovation. A recent report by Consumer NZ highlighted that 78% of Kiwis support increased funding for Pharmac to access newer medications faster.
Controversial Take: Balancing Cost and Innovation
Critics argue that Pharmac's conservative approach limits access to new therapies, particularly for rare diseases. Conversely, supporters emphasize the importance of fiscal prudence and equitable access. The middle ground lies in fostering partnerships with pharmaceutical companies to negotiate better pricing and expedite the introduction of innovative treatments.
8. public health and Preventative Care
New Zealand's approach to public health emphasizes preventative care, with initiatives targeting smoking cessation, obesity reduction, and immunization. The government's Smokefree 2025 goal exemplifies this commitment, aiming to reduce smoking prevalence to less than 5%. However, achieving these targets requires sustained efforts in education, policy, and community engagement.
Myths and Realities
- Myth: "All healthcare services are free in New Zealand." Reality: While many services are subsidized, out-of-pocket costs exist for prescriptions, dental care, and some specialist services.
- Myth: "Private insurance covers everything." Reality: Private insurance mainly covers elective procedures and specialist consultations, not emergency care or GP visits.
- Myth: "Telehealth is only for the tech-savvy." Reality: Telehealth is designed to be user-friendly, with support available for those with limited digital skills.
Future Trends and Predictions
By 2028, New Zealand's healthcare system is expected to see significant advancements in personalized medicine, driven by genetic research and data analytics. The integration of AI and machine learning will further enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment personalization, necessitating investments in digital infrastructure and workforce training.
Conclusion
New Zealand's healthcare system, while robust, faces ongoing challenges that require innovative solutions and sustained public investment. By understanding the complexities and leveraging technology and policy reforms, New Zealand can continue to provide high-quality healthcare to all its citizens. What are your thoughts on New Zealand's healthcare future? Share your insights below!
Related Search Queries
- New Zealand healthcare system overview
- Public vs. private healthcare in NZ
- Telehealth adoption in New Zealand
- mental health initiatives NZ
- Pharmac funding challenges
People Also Ask
What are the biggest challenges facing New Zealand's healthcare system?Funding constraints, health disparities, and workforce shortages are among the key challenges, as highlighted by the Ministry of Health.
How does New Zealand's healthcare system compare globally?New Zealand's healthcare system ranks high for accessibility and quality, yet faces challenges similar to other countries, such as rising costs and demand.
What future developments are expected in New Zealand's healthcare system?Advancements in technology, personalized medicine, and telehealth are expected to shape the future, enhancing patient care and system efficiency.