New Zealand's commitment to sustainability and its unique geographical features make the optimization of its power grid not just necessary, but imperative. As the nation progresses towards a more sustainable future, the design of a more efficient power grid is crucial. This article delves into the intricacies of crafting a modern power grid, addressing local challenges and opportunities, and providing actionable insights for policymakers.
Understanding New Zealand's Current Power Grid Landscape
New Zealand's power grid is characterized by its reliance on renewable energy sources. As of 2022, approximately 84% of the country's electricity came from renewable sources such as hydroelectric, geothermal, and wind power (Source: Stats NZ). This places New Zealand among the world leaders in renewable energy utilization. However, the distribution and efficiency of the power grid remain areas ripe for innovation and improvement.
Challenges in the Current System
- Geographical Barriers: New Zealand's diverse terrain presents significant challenges in energy distribution, particularly in remote and rural areas.
- Infrastructure Aging: Much of the power grid infrastructure is aging, necessitating updates to accommodate modern technological advancements.
- Demand Fluctuation: Seasonal and unpredictable demand fluctuations can strain the grid, leading to inefficiencies.
Innovative Solutions for a More Efficient Power Grid
To enhance the efficiency of New Zealand's power grid, several advanced solutions can be implemented. These solutions leverage technology and innovative design to address current challenges.
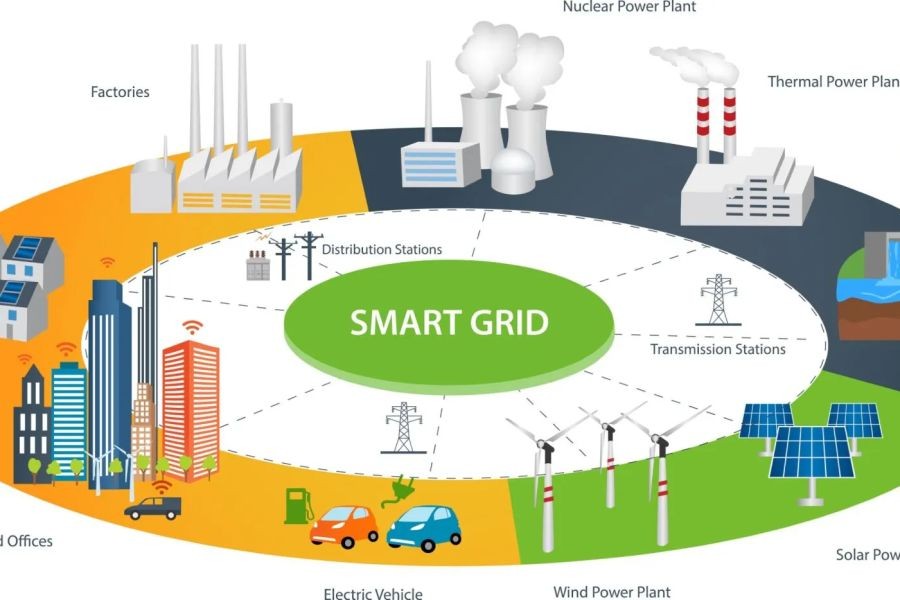
Smart Grid Technology
Smart grids utilize digital technology to monitor and manage the transport of electricity from all generation sources to meet varying electricity demands. By employing smart meters and advanced data analytics, New Zealand can optimize energy distribution, reduce losses, and improve reliability.
Decentralized Energy Systems
Decentralized energy systems, such as microgrids, offer an opportunity to enhance energy reliability and resilience. These systems can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, providing localized solutions and reducing transmission losses.
Energy Storage Solutions
Integrating energy storage systems, such as batteries, can significantly improve grid efficiency by storing excess energy during low demand and releasing it during peak periods. This not only balances supply and demand but also stabilizes the grid.
Case Study: Vector Limited's Smart Grid Initiative
Problem: Vector Limited, a leading New Zealand energy company, faced challenges with grid reliability and efficiency, especially during peak demand periods.
Action: To address these issues, Vector Limited implemented smart grid solutions, including the deployment of advanced metering infrastructure and real-time data analytics.
Result: The initiative led to a 15% reduction in energy losses and improved grid reliability by 20%, demonstrating the potential of smart grid technology in enhancing efficiency (Source: Vector Limited Annual Report).
Takeaway: This case study highlights the impact of smart grid technology in improving energy efficiency and reliability, offering valuable insights for policymakers aiming to enhance New Zealand's power grid.
Debunking Common Myths About Power Grid Efficiency
- Myth: "Renewable energy alone can solve all efficiency issues." Reality: While renewable energy is crucial, its intermittent nature necessitates complementary technologies such as smart grids and energy storage to ensure consistent efficiency.
- Myth: "Upgrading the power grid is too costly." Reality: Although initial investments are required, long-term savings from reduced energy losses and enhanced grid reliability outweigh the costs.
Future Trends: The Path Forward for New Zealand
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into power grid management is poised to revolutionize efficiency. By 2030, it is predicted that AI-driven systems will optimize energy distribution, reducing costs and enhancing reliability by up to 30% (Source: MBIE Future Energy Report).
Harnessing AI for Predictive Maintenance
AI technologies can predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. This proactive approach ensures uninterrupted energy supply and enhances grid resilience.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Energy Future
New Zealand stands at the forefront of renewable energy adoption, yet optimizing its power grid remains a critical challenge. By embracing smart grid technology, decentralized systems, and energy storage, the nation can enhance grid efficiency, ensuring a reliable and sustainable energy future. Policymakers must prioritize these innovations to meet the growing energy demands and achieve environmental goals.
What’s your take? How can New Zealand further enhance its power grid efficiency? Share your insights below!
People Also Ask (FAQ)
- How does smart grid technology benefit New Zealand's power grid?Smart grid technology enhances efficiency by optimizing energy distribution, reducing losses, and improving reliability through advanced metering and data analytics.
- What are the biggest misconceptions about renewable energy in power grids?A common myth is that renewable energy alone can solve all efficiency issues. However, complementary technologies like smart grids and storage systems are essential for consistent efficiency.
Related Search Queries
- New Zealand power grid efficiency
- Smart grid technology in New Zealand
- Energy storage solutions NZ
- Decentralized energy systems
- Future of renewable energy in NZ