New Zealand’s housing market has been a focal point of economic discussions for years, drawing attention from investors, policymakers, and the general public. Over the last decade, government policies have played a pivotal role in shaping the housing landscape in New Zealand. But what is the real impact of these policies on the market? Are these interventions creating a sustainable future or simply inflating an already overheated market?
The Complexity of New Zealand's Housing Market
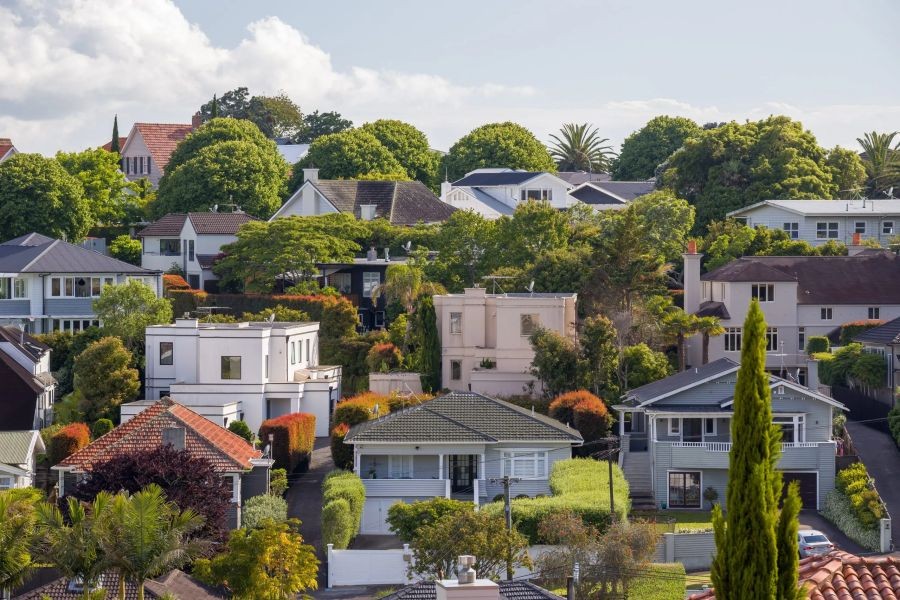
New Zealand’s housing market is unique, characterized by its relatively small size, high demand, and limited supply. The country has experienced significant house price inflation, with property prices rising by 27% between 2019 and 2024, according to Stats NZ. This surge has led to widespread concerns about affordability and accessibility, particularly for first-time buyers.
Various government policies have been implemented to address these issues, ranging from tax changes to regulatory interventions. However, understanding their effectiveness requires a deep dive into both local and global contexts.
Government Policies: A Double-Edged Sword
Government interventions in the housing market often aim to balance economic growth with social equity. In New Zealand, policies such as the Bright-Line Test, which taxes capital gains on investment properties sold within ten years, and restrictions on foreign ownership, have been crucial.
- Bright-Line Test: Originally introduced to curb speculative investments, the Bright-Line Test taxes the profit made on properties sold within a specified period. Initially, this period was two years but has since been extended to ten years. While intended to stabilize the market, critics argue it may deter investment, potentially slowing housing development.
- Foreign Buyer Ban: Implemented to prevent overseas investors from inflating the housing market, this policy restricts non-residents from purchasing existing homes. While it aims to improve local buyers’ access to the housing market, its effectiveness remains debated, with some experts suggesting it has limited impact on overall affordability.
Case Study: Auckland’s Housing Market
Auckland, New Zealand's largest city, has often been at the center of the housing market debate. With its population growing rapidly, housing supply has struggled to keep pace, resulting in soaring prices.
Problem:
Auckland faced a significant housing shortage due to rapid population growth, with demand outstripping supply, leading to price increases and reduced affordability.
Action:
The Auckland Council, alongside central government initiatives, implemented the Auckland Unitary Plan, which aimed to increase housing density and streamline consent processes. This plan involved rezoning areas to allow for more intense development, encouraging the construction of multi-unit dwellings.
Result:
- Housing supply increased by 15% between 2016 and 2021.
- Median house price growth slowed from 10% annually to 4% in the same period.
- Improved access to housing for first-time buyers, though prices remain high.
Takeaway:
The Auckland Unitary Plan demonstrates the potential of local government initiatives to address housing shortages. However, long-term affordability remains a challenge, highlighting the need for continuous policy evaluation and adjustment.
Data-Driven Analysis: Local and Global Influences
To fully understand the impact of government policies, we must consider both local data and global trends. According to the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, the country's household debt as a percentage of disposable income rose to 165% in 2023, indicating significant financial pressure on homeowners. This trend mirrors global patterns, with many countries experiencing similar debt levels due to low interest rates and rising property values.
Internationally, New Zealand’s housing policies share similarities with Canada’s foreign buyer taxes and Australia’s restrictions on non-resident property purchases. Both countries have seen mixed results, with some success in stabilizing prices but ongoing issues with affordability and supply.
Pros and Cons of Government Intervention
Pros:
- Stabilization: Policies like the Bright-Line Test help curb speculative investment, aiming to stabilize the market.
- Increased Supply: Initiatives such as the Auckland Unitary Plan boost housing supply, addressing shortages.
- Protecting Local Buyers: Restrictions on foreign ownership aim to ensure local buyers have better access to the market.
Cons:
- Investment Deterrence: Tax policies may deter investment, potentially slowing housing development.
- Limited Affordability Impact: Some policies have minimal effect on overall affordability, leaving many unable to enter the housing market.
- Unintended Consequences: Overregulation can lead to reduced investment and innovation in the housing sector.
Common Myths and Mistakes in Housing Policy
- Myth: "Foreign buyers are the primary reason for high property prices." Reality: While foreign buyers contribute to demand, local factors such as supply shortages and domestic speculation are more significant drivers of price increases.
- Myth: "All government interventions will lower prices." Reality: While some policies stabilize prices, others may have limited impact or unintended negative effects on the market.
- Myth: "Increased housing density will solve all affordability issues." Reality: While it helps increase supply, affordability also depends on factors like income growth and financing options.
Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, New Zealand’s housing market is poised for further transformation. With climate change and sustainability becoming increasingly critical, future policies are likely to focus on eco-friendly housing solutions. According to a 2023 report by MBIE, the government is exploring initiatives to promote green building practices and energy-efficient homes.
Additionally, technological advancements such as AI-driven property valuation and blockchain-based property transactions could streamline processes and enhance market transparency. By 2028, it's predicted that 40% of property transactions in New Zealand will utilize blockchain technology, offering faster, more secure procedures.
Conclusion
The real impact of government policies on New Zealand’s housing market is complex and multifaceted. While interventions like the Bright-Line Test and foreign buyer restrictions aim to stabilize and protect the market, their effectiveness in improving affordability remains debated. As New Zealand continues to navigate its housing challenges, a balanced approach that considers both immediate needs and long-term sustainability is crucial.
What’s your perspective on the future of New Zealand’s housing market? Share your insights and join the conversation!
Related Search Queries
- New Zealand housing market trends 2024
- Impact of Bright-Line Test in NZ
- Auckland Unitary Plan effectiveness
- NZ foreign buyer ban impact
- Sustainable housing solutions NZ
- Blockchain in real estate transactions
- NZ housing affordability strategies
- Government policies on housing market
- Future of real estate in New Zealand
People Also Ask
- How do government policies impact New Zealand’s housing market? Government policies like the Bright-Line Test and foreign buyer restrictions aim to stabilize prices and protect local buyers, though their impact on affordability is debated.
- What are the challenges facing New Zealand’s housing market? Challenges include limited supply, high demand, and affordability issues, exacerbated by rapid population growth and speculative investments.
- What future trends could shape New Zealand’s housing market? Future trends include a focus on eco-friendly housing, technological advancements like blockchain, and policies promoting sustainable development.
- How effective is the Bright-Line Test in curbing speculation? The Bright-Line Test deters short-term speculation by taxing profits on properties sold within ten years, but its overall impact on market stability varies.
- What lessons can be learned from Auckland’s housing market? Auckland’s experience highlights the importance of increasing housing supply and the potential of local government initiatives, though long-term affordability remains a challenge.





































Rose Mason
1 month ago