Fast fashion, characterized by the rapid production of inexpensive clothing to meet ever-changing trends, has been a significant disruptor in the global retail industry. While it might seem like a cost-effective way to keep up with fashion trends, it has hidden financial consequences that can impact your wallet more than you might realize. As an angel investor with an eye on market trends and financial impacts, understanding the broader implications of fast fashion is crucial, especially in the Australian context where consumer behavior and economic policies play a unique role.
The True Cost of Fast Fashion in Australia
Fast fashion's allure of affordability and accessibility comes at a price, not just to the environment but to consumers' finances as well. In Australia, where the fashion industry contributes significantly to the economy, the impact of fast fashion is particularly noteworthy. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, the retail turnover for clothing, footwear, and personal accessory retailing in Australia was around AUD 25 billion in 2022. However, the rapid turnover of fashion items and the race to keep up with trends can lead to financial pitfalls for consumers.
1. The Illusion of Savings
Fast fashion often gives the illusion of savings with its low prices. However, the cost per wear of these items tends to be higher due to their poor quality and short lifespan. A study by CHOICE, Australia’s leading consumer advocacy group, found that fast fashion garments are typically worn only seven times before being discarded. This frequent replacement cycle can lead to increased spending over time.
2. Impact on Personal Finances
The rapid turnover of fashion trends can lead to compulsive buying habits, impacting personal savings and financial health. A report by the Reserve Bank of Australia highlighted that consumer debt levels have been rising, with discretionary spending on fashion playing a role. Consumers often underestimate the cumulative impact of multiple low-cost purchases, which can add up significantly over the year.
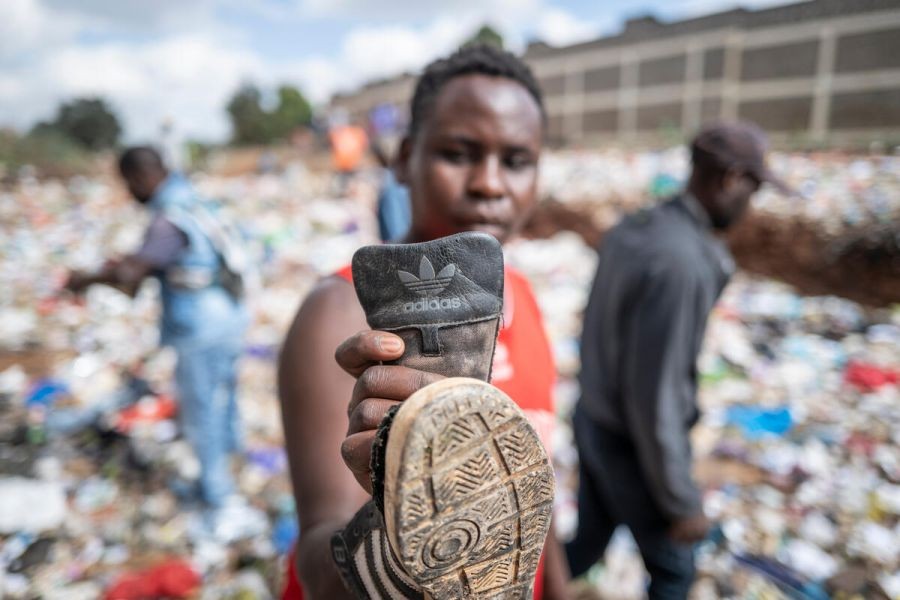
3. Environmental Costs and Hidden Expenses
The environmental impact of fast fashion also translates into hidden financial costs. The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) has been investigating the misleading environmental claims by some fast fashion brands. As environmental regulations tighten, these brands may pass on compliance costs to consumers, resulting in higher prices.
4. Economic Implications
Fast fashion's business model has broader economic implications for Australia. The influx of cheap imports can affect local manufacturers and retailers, leading to job losses and reduced economic activity. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that the manufacturing sector has been declining, partly due to competition from low-cost imports. This decline affects the local economy and can lead to increased unemployment rates.
5. Impact on Investment Opportunities
For investors, the fast fashion trend presents a mixed bag. While some brands may offer short-term gains, the long-term sustainability and ethical concerns can pose risks. Investment in companies with poor environmental practices may lead to reputational risks and potential financial losses as consumer preferences shift towards sustainable fashion. This shift is already visible, with Australian consumers increasingly favoring ethical brands, as noted by a recent survey conducted by Sydney's Institute for Sustainable Futures.
Case Study: The Australian Fashion Industry's Response
As fast fashion faces increasing scrutiny, some Australian companies have been leading the charge towards sustainability. One notable example is Outland Denim, a Queensland-based company that focuses on ethical production and environmental sustainability. By investing in sustainable practices and transparent supply chains, Outland Denim has not only built a loyal customer base but also attracted investment from socially responsible investors.
Problem:
Outland Denim struggled with brand recognition in a market dominated by fast fashion giants.
Action:
They focused on creating high-quality, sustainable denim products and leveraged social media to highlight their ethical practices.
Result:
Outland Denim saw a 200% increase in sales within two years and secured investment from prominent figures, including Meghan Markle's endorsement.
Takeaway:
This case study demonstrates the growing consumer and investor demand for sustainable fashion. Australian companies that prioritize ethical practices can not only thrive in the local market but also on the global stage.
Pros and Cons of Fast Fashion
Pros:
- Affordability: Offers affordable clothing options for budget-conscious consumers.
- Variety: Provides a wide range of styles and trends to choose from.
- Accessibility: Easily accessible in multiple retail stores and online platforms.
Cons:
- Quality: Often lower quality, leading to frequent replacements.
- Environmental Impact: Contributes significantly to environmental degradation.
- Financial Strain: Encourages impulsive buying and increased spending.
- Economic Impact: Can lead to job losses in local manufacturing sectors.
Debunking Common Myths
Myth: Fast fashion is cost-effective in the long run.
Reality: While fast fashion items are cheaper upfront, their short lifespan means you spend more over time replacing them.
Myth: Fast fashion meets consumer demand for new trends.
Reality: It creates artificial demand by frequently changing styles, leading to unnecessary purchases.
Myth: Fast fashion doesn't impact the local economy.
Reality: The decline in local manufacturing due to fast fashion imports has contributed to job losses in Australia.
Future Trends and Predictions
As awareness of fast fashion's financial and environmental costs grows, consumers and investors are likely to shift towards more sustainable options. By 2030, it's predicted that 50% of the Australian fashion market will consist of sustainable brands, driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressures from bodies like the ACCC and APRA.
Conclusion
While fast fashion may seem like a wallet-friendly choice, its hidden costs can outweigh the perceived savings. For Australian consumers and investors, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed decisions. By supporting sustainable fashion, you not only contribute to a healthier planet but also make a sound financial choice.
What's your take on the fast fashion industry? Have you experienced its financial impacts firsthand? Share your insights below!
People Also Ask (FAQ)
How does fast fashion impact businesses in Australia?
Fast fashion affects Australian businesses by increasing competition with low-cost imports, impacting local manufacturers, and driving changes in consumer preferences towards more sustainable options.
What are the biggest misconceptions about fast fashion?
One common myth is that fast fashion is cost-effective long-term. However, frequent replacements and poor quality often lead to higher overall spending.
Who benefits the most from fast fashion?
Fast fashion primarily benefits companies that capitalize on rapid production cycles and low-cost imports, though it often comes at the expense of local manufacturers and the environment.
Related Search Queries
- Fast fashion impact on economy
- Sustainable fashion brands in Australia
- Environmental cost of fast fashion
- How to invest in ethical fashion
- Trends in the Australian fashion industry
- Fast fashion vs. sustainable fashion
- Economic effects of fast fashion in Australia
- Consumer behavior and fashion trends
- Impact of fast fashion on local businesses
- Future of the fashion industry in Australia