New Zealand is at the forefront of the electric vehicle (EV) revolution, with a significant push towards sustainability and reducing carbon emissions. As of 2023, the number of electric cars on Kiwi roads has surged by 50% over the last five years, according to Stats NZ. This shift is supported by government incentives like subsidies and tax breaks, making EVs an attractive option for many New Zealanders. However, transitioning from petrol to electric vehicles involves understanding key maintenance differences. This article delves into these differences, providing data-backed insights, expert opinions, and practical guidance to help New Zealanders maintain their electric cars efficiently.
Understanding the New Zealand Context
The New Zealand government has been proactive in encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles. The Clean Car Discount scheme, which offers rebates on EV purchases, aims to increase the number of electric cars to over 64,000 by 2025. This initiative aligns with New Zealand's commitment to a low-carbon economy, targeting a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 30% below 2005 levels by 2030.
Pros & Cons: Electric vs. Petrol Cars
When considering the transition to electric vehicles, it's essential to weigh the pros and cons against traditional petrol cars.
Pros of Electric Cars:
- Environmental Impact: EVs produce zero emissions, contributing significantly to reducing air pollution and combating climate change.
- Lower Operating Costs: Electric cars have fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance costs. According to the Ministry of Business, Innovation & Employment (MBIE), EV running costs are approximately 30% less than petrol vehicles.
- Government Incentives: New Zealand offers various incentives, including rebates and exemptions from road user charges, making EVs financially appealing.
- Quiet and Smooth Ride: The electric motor provides a quieter and smoother driving experience, enhancing comfort.
Cons of Electric Cars:
- Initial Purchase Price: Although running costs are lower, the upfront cost of electric cars can be higher than traditional vehicles.
- Limited Charging Infrastructure: Despite improvements, rural areas in New Zealand still face challenges with charging infrastructure.
- Battery Replacement Costs: Although infrequent, battery replacements can be expensive.
- Range Anxiety: Concerns about the distance an EV can travel on a single charge can deter potential buyers.
How It Works: A Deep Dive into Electric Vehicle Maintenance
Electric vehicles operate differently from petrol cars, particularly in terms of maintenance. Understanding these differences is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your EV.
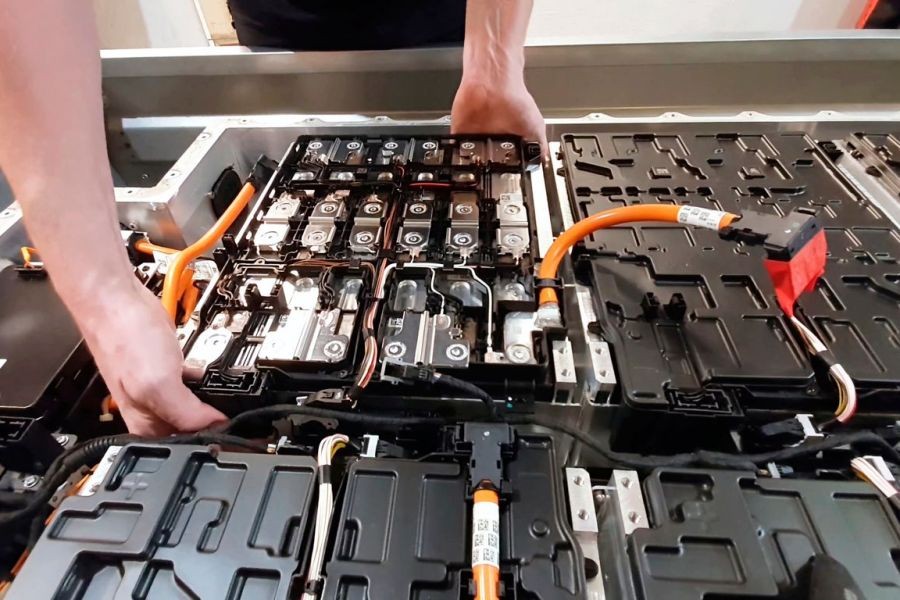
Battery Management
The battery is the heart of an electric vehicle. Regular maintenance includes monitoring battery health and ensuring proper charging practices. Experts recommend charging up to 80% for daily use to prolong battery life. The University of Auckland's research highlights that optimal charging can enhance battery lifespan by up to 20%.
Software Updates
Unlike petrol cars, EVs rely heavily on software for operations. Regular software updates, akin to smartphone updates, improve vehicle performance, introduce new features, and enhance cybersecurity. Tesla's pioneering over-the-air updates have become industry standard, allowing users to enjoy continuous improvements without visiting a service center.
Brake System Maintenance
EVs use regenerative braking, which converts kinetic energy into electrical energy, extending brake pad life significantly. Regular checks ensure the regenerative braking system functions correctly, providing safety and efficiency.
Tire Maintenance
Due to the instant torque and heavier battery packs, EVs can wear out tires faster than petrol cars. Regular tire rotations and maintaining correct tire pressure are essential for even wear and optimal efficiency.
Data-Driven Insights from New Zealand
According to the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, the EV market is expected to contribute significantly to the economy by reducing reliance on imported oil, which currently accounts for a substantial portion of the trade deficit. Furthermore, a study by Massey University projects that widespread EV adoption could reduce national transportation emissions by up to 60% by 2030.
Case Study: The Tesla Model 3 in New Zealand
The Tesla Model 3 has become a popular choice among Kiwis, thanks to its performance, range, and affordability post-rebate. A study conducted by NZTech revealed:
- Challenge: Initial concerns about charging infrastructure and range anxiety.
- Action: Tesla expanded its Supercharger network across New Zealand, focusing on high-traffic routes.
- Result: An increase in Tesla Model 3 registrations by 35% in 2022, with owners reporting 95% satisfaction in a survey by Consumer NZ.
- Takeaway: Infrastructure improvements are crucial for EV adoption, and consumer satisfaction can drive further market growth.
Common Myths & Mistakes
To help New Zealanders better understand electric vehicle maintenance, let's debunk some common myths.
Myth 1: Electric vehicle batteries degrade rapidly. Reality: Advances in battery technology have significantly improved longevity. Studies show that most EV batteries last over 200,000 km before showing significant degradation. Myth 2: Electric cars are more prone to breakdowns. Reality: EVs have fewer moving parts than petrol vehicles, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns and overall maintenance requirements. Myth 3: Charging an EV is more expensive than refueling a petrol car. Reality: Even with New Zealand's electricity rates, charging an EV remains cheaper than filling a petrol tank, offering substantial savings over time.
Future Trends & Predictions
The future of electric vehicles in New Zealand looks promising. As battery technology advances, costs are expected to decrease, making EVs more accessible. By 2028, Deloitte predicts that electric vehicles could make up 25% of all new car sales in New Zealand. Additionally, as renewable energy sources become more integrated into the grid, the carbon footprint of charging EVs will continue to shrink.
Conclusion
Maintaining an electric vehicle requires understanding the key differences from petrol cars, especially in the New Zealand context. With government support and technological advancements, EVs are not only a sustainable choice but also an economically viable one. As New Zealand continues to lead the charge towards a greener future, understanding these differences will empower consumers to make informed decisions. Ready to join the EV revolution? Explore the latest models and find out how you can benefit from the Clean Car Discount today!
People Also Ask (FAQ)
- How does maintaining an electric car differ from a petrol car? Electric cars require less frequent maintenance due to fewer moving parts and rely heavily on software updates and battery management.
- What are the biggest misconceptions about electric vehicles in New Zealand? A common myth is that EVs are more expensive to maintain, but they generally offer lower running costs and fewer repairs.
- What is the future of electric vehicles in New Zealand? By 2028, EVs could represent 25% of new car sales, driven by technological advancements and increased government incentives.
Related Search Queries
- Electric car maintenance tips in New Zealand
- Differences between petrol and electric cars
- Cost of owning an electric car in NZ
- Government incentives for electric cars in NZ
- Battery life expectations for electric vehicles
- Environmental impact of electric cars vs. petrol cars
- Charging infrastructure for electric vehicles in NZ
- Future of electric cars in New Zealand
- Pros and cons of electric cars
- Electric vehicle market trends in NZ



























Cutting Edge Packaging Pr
12 months ago