Australia is known for its sprawling landscapes and dynamic cities, but it is also notorious for having some of the most expensive toll roads in the world. This isn’t just a gripe for daily commuters; it has significant implications for the export and trade sectors. High toll costs can inflate logistics expenses, impacting the competitive edge of Australian businesses globally. So, what makes these tolls so costly, and how does this affect the broader economic landscape?
Understanding the Cost Structure of Australian Toll Roads
There are several factors contributing to the high costs of toll roads in Australia. One primary reason is the privatization of these roads. Unlike many countries where toll roads are government-operated, in Australia, private companies often manage them, aiming for profitability. This leads to higher tolls as businesses seek returns on their investments. According to a 2023 report by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), approximately 72% of toll roads in Australia are privately owned, significantly higher than the global average of 40%.
Privatization and Its Economic Impact
The privatization model has its advantages, such as improved road maintenance and efficiency. However, it also results in toll rates that are often out of reach for the average commuter and increase the operational costs for businesses reliant on road transport. A study by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) found that logistics costs for Australian businesses are 15% higher than in countries with government-operated toll roads.
Case Study: Transurban and Sydney’s Motorways
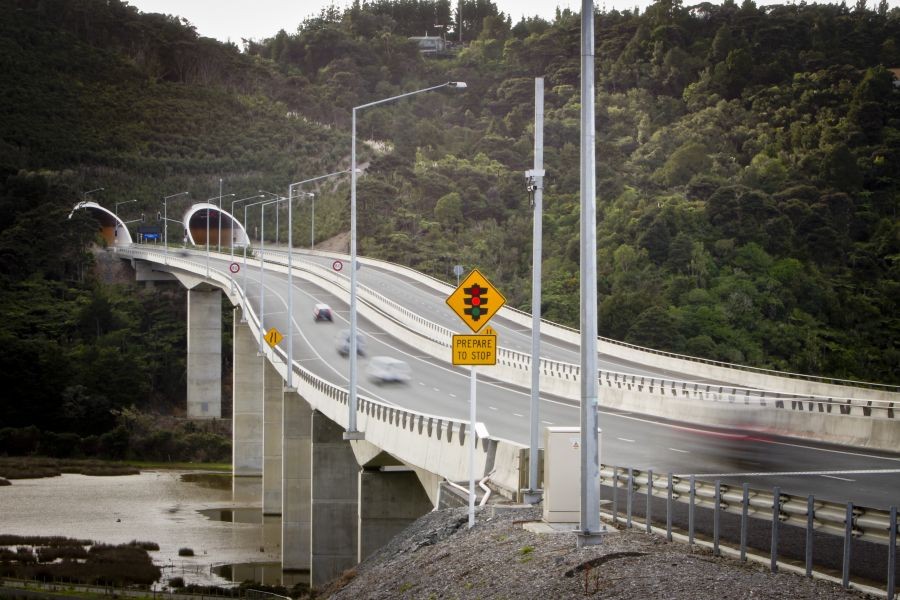
One of the most notable examples is Transurban, a leader in the toll road sector. Transurban manages several major motorways in Sydney, including the M2, M5, and WestConnex. These roads are crucial for freight companies transporting goods across New South Wales. However, the high toll rates have drawn criticism. For instance, the M5 motorway charges heavy vehicles up to AUD 23.49 for a single journey, a significant expense for logistics companies making multiple trips daily.
Action: To mitigate these costs, some companies have started adopting alternative strategies, such as optimizing route planning and using toll-free roads when feasible. Transurban has also introduced dynamic pricing models to incentivize off-peak travel, aiming to distribute traffic more evenly throughout the day.
Result: After implementing these strategies, companies have reported up to a 10% reduction in logistics costs. Transurban’s dynamic pricing has also led to a 5% increase in off-peak travel, easing congestion during peak hours.
Takeaway: The case study underscores the importance of innovative pricing strategies and logistics optimization in managing toll expenses. It also highlights the need for businesses to adapt to the realities of a privatized toll system.
Regulatory Insights: ACCC’s Role in Managing Toll Road Competition
The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) plays a crucial role in monitoring toll road pricing and ensuring fair competition. However, despite their oversight, the complexity of private-public partnerships can lead to pricing structures that challenge regulatory efforts. This dynamic was evident in the 2022 inquiry into Sydney’s toll roads, where the ACCC found that lack of competition often resulted in higher prices for consumers.
Pros and Cons of Toll Road Pricing
- Pros:
- Revenue Generation: Toll roads generate significant revenue for infrastructure development.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Private management often leads to better-maintained roads.
- Traffic Management: Tolls can help in managing traffic congestion.
- Cons:
- High Costs: Increased operational costs for logistics and trade due to high toll rates.
- Limited Routes: Few alternatives to tolled roads can lead to monopolistic pricing.
- Economic Divide: High tolls can disproportionately affect lower-income individuals and small businesses.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Toll Roads in Australia
The future of toll roads in Australia might see a shift driven by technological advancements and policy changes. The introduction of electric and autonomous vehicles may alter traffic patterns and toll structures. Moreover, the Australian government is considering more robust regulatory frameworks to enhance competition and potentially cap excessive pricing. According to a Deloitte 2024 report, by 2030, Australia might see a 20% reduction in toll road costs due to increased competition and technological integration.
Conclusion: Navigating the Toll Road Challenges
The high cost of toll roads in Australia poses a significant challenge for businesses, particularly in the transport and export sectors. However, by understanding the underlying causes and potential future trends, businesses can better strategize to mitigate these costs. As the landscape evolves, staying informed and adaptable will be key to maintaining a competitive edge.
Final Takeaways
- Understanding the Market: Recognize the impact of privatization on toll costs.
- Strategize Logistics: Optimize routing to manage toll expenses effectively.
- Regulatory Awareness: Stay updated on ACCC regulations and potential policy changes.
- Future Readiness: Prepare for technological shifts impacting toll road dynamics.
People Also Ask (FAQ)
Why are toll roads expensive in Australia?
High toll rates in Australia are primarily due to privatization, where private companies manage these roads for profit, leading to higher costs compared to government-operated roads.
How do toll roads affect Australian businesses?
High toll costs increase logistics expenses, impacting the competitiveness of Australian businesses, particularly in export and trade sectors reliant on road transport.
Related Search Queries
- Why are Australian toll roads so expensive?
- Impact of toll roads on Australian businesses
- How does toll pricing work in Australia?
- Toll road privatization in Australia
- Future of toll roads in Australia
As Australia continues to navigate these challenges, businesses and policymakers must collaborate to find sustainable solutions that balance profitability with accessibility and economic growth.




























melvadycus5364
11 months ago