In the dynamic landscape of public transport systems, New Zealand and Australia have often been compared. With both nations boasting unique geographic and demographic characteristics, the efficiency and reliability of their public transport systems have become points of national pride and necessary infrastructure for economic growth. But which country does it better? This article delves into a comparative analysis, exploring the nuances of public transport systems in New Zealand and Australia, with a particular focus on how these systems impact financial advisors and the broader economic landscape.
🔍 Understanding the Stakes: Why Public Transport Matters
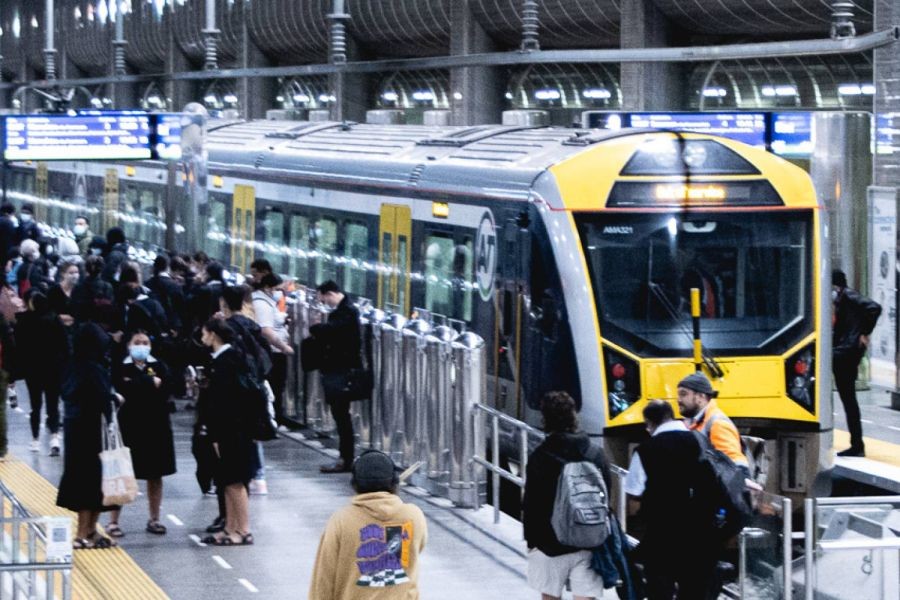
In New Zealand, public transport plays a crucial role in supporting economic activities across major cities like Auckland, Wellington, and Christchurch. According to Stats NZ, public transport usage increased by 8.5% in 2022, underscoring its importance in urban mobility. For financial advisors, the correlation between efficient public transport and economic vitality is clear: better transport systems can lead to increased productivity, reduced operational costs for businesses, and enhanced property values.
Australia, with its vast landmass and urban centers like Sydney and Melbourne, faces different challenges and opportunities. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reported that public transport trips constituted 15% of urban travel in 2021, indicating a significant reliance on these systems for daily commutes. For financial advisors, understanding these dynamics is critical when advising on property investments, business location strategies, and urban development projects.
🧠 Unique Expert Insights & Industry Deep Dive
One of the standout features of New Zealand's public transport system is its focus on sustainability and integration. The Auckland Transport Alignment Project (ATAP) aims to create a cohesive transport network by 2050, prioritizing electric and hybrid buses to reduce carbon footprints. This move aligns with New Zealand’s broader environmental policies, which include a target to become carbon neutral by 2050. Financial advisors should note that such initiatives could drive investment opportunities in green technologies and sustainable infrastructure projects.
In contrast, Australia's public transport system has been praised for its technological integration and innovation. Sydney's Opal card system, for instance, provides seamless travel across various modes of transport, including trains, buses, and ferries. This integration not only enhances user convenience but also offers data analytics capabilities that can be leveraged for better urban planning and real-time service improvements. Advisors can find value in understanding these technological advancements as they could herald similar opportunities in New Zealand, particularly in cities like Auckland and Wellington.
📊 Who's Leading? A Data-Driven Comparison
When comparing the efficiency of public transport systems, key metrics such as coverage, frequency, and user satisfaction come to the fore. According to the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE), New Zealand's urban transport systems are among the most accessible, covering approximately 95% of urban areas. However, Australia often leads in frequency, with cities like Melbourne offering train services every 10 minutes during peak hours.
Cost efficiency is another critical area. A report from the Reserve Bank of New Zealand highlights that the average cost of a monthly public transport pass in New Zealand is lower than in major Australian cities, making it a more attractive option for daily commuters. This aspect is particularly relevant for financial advisors who must consider the cost-benefit analysis when advising clients on relocation or business expansion.
🔄 Balancing the Scales: Pros vs. Cons Analysis
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each system can offer valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
✅ Pros of New Zealand's System:
- Sustainability Focus: Initiatives like ATAP emphasize eco-friendly transport solutions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower average costs for public transport passes.
- Comprehensive Coverage: High accessibility across urban areas.
❌ Cons of New Zealand's System:
- Lower Frequency: Less frequent services compared to Australian cities.
- Limited Technological Integration: Room for improvement in tech-driven solutions.
✅ Pros of Australia's System:
- Technological Innovation: Advanced systems like Sydney’s Opal card.
- High Frequency: Frequent services enhance user convenience.
❌ Cons of Australia's System:
- Higher Costs: Monthly passes tend to be more expensive.
- Geographic Limitations: Vast distances can lead to longer travel times.
📖 Real-World Case Studies
Case Study: Auckland's Electric Buses – Pioneering Sustainability
Problem: Auckland faced rising pollution levels and public demand for cleaner transport solutions.
Action: The city implemented electric buses, part of the ATAP’s sustainability goals.
Result: Within a year, carbon emissions from buses were reduced by 20%.
Takeaway: This initiative highlights the potential for investment in green technologies, offering significant economic and environmental benefits.
Case Study: Sydney's Opal System – Leading Technological Integration
Problem: Sydney needed a unified ticketing system to streamline public transport use.
Action: The Opal card was introduced, integrating all modes of public transport under one system.
Result: Public transport usage increased by 15% within two years, demonstrating the system’s effectiveness.
Takeaway: Technological advancements in transport can significantly enhance user experience and operational efficiency.
🔮 Future Trends & Predictions
Looking ahead, both New Zealand and Australia are poised for transformative changes in their public transport systems. By 2030, New Zealand aims to have 50% of its public transport fleet electrified, according to a report by MBIE. This shift is expected to create opportunities for investments in renewable energy and electric vehicle infrastructure.
In Australia, the focus will likely be on expanding urban rail networks and integrating AI-driven technology to optimize routing and scheduling. A study by Deloitte predicts that AI integration could reduce operational costs by up to 30%, offering substantial savings for government and private transport operators.
🔍 Common Myths & Mistakes
Myth: "Public transport is only for low-income individuals."
Reality: In urban centers across New Zealand and Australia, public transport is widely used by professionals and students alike, offering convenience and cost savings.
Myth: "Investing in public transport is not profitable."
Reality: With the rise of sustainable and tech-driven solutions, public transport investments are yielding high returns, particularly in infrastructure and green technology.
Myth: "Public transport is always cheaper than driving."
Reality: While generally more cost-effective, the financial benefits depend on factors like distance, frequency, and available subsidies.
📖 Conclusion
As we evaluate the public transport systems of New Zealand and Australia, it's clear that each has its distinct strengths and challenges. For financial advisors, understanding these nuances is critical to making informed decisions about investments, property values, and urban development strategies. The drive towards sustainability and technological integration offers exciting opportunities for growth and innovation. What’s your take on the future of public transport in these regions? Share your insights below!
🔍 People Also Ask (FAQ)
How does public transport impact businesses in New Zealand?
Efficient public transport in New Zealand enhances business productivity by reducing commute times and operational costs, contributing to overall economic growth.
What are the biggest misconceptions about public transport?
One common myth is that public transport is only for low-income individuals. However, it's widely used by professionals and students for its convenience and cost-efficiency.
What are the best strategies for implementing public transport improvements?
Experts recommend starting with sustainable initiatives like electrification, followed by tech integration for real-time data analytics, ensuring long-term success.
🔍 Related Search Queries
- New Zealand public transport vs Australia
- Public transport systems in New Zealand and Australia
- Economic impact of public transport in New Zealand
- Sustainable transport solutions in New Zealand
- Technological advancements in Australian public transport
- Public transport investment opportunities
- Electric buses in New Zealand
- Opal card system in Sydney
- Future of transport in New Zealand
- Public transport cost efficiency