As New Zealand continues to evolve into a hub for innovation, the emergence of smart housing developments is reshaping the residential landscape. With sustainability, technology, and community living at its core, New Zealand's smart housing initiatives offer a blueprint for modern living. Yet, are these developments a viable solution for the country's housing issues? This article delves into the intricacies of New Zealand’s smart housing, offering insights for management consultants and decision-makers.
Introduction
Imagine a future where homes are not only energy-efficient but also integrated with technology that enhances daily life. This is becoming a reality in New Zealand, where smart housing developments are on the rise. However, these advances are not just about technology; they are deeply intertwined with sustainability and community development. With the housing market facing challenges such as affordability and environmental impact, these smart solutions could be pivotal.
New Zealand’s commitment to sustainability is evident in its policies. The Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE) has reported a targeted approach towards reducing carbon emissions, with residential sectors playing a significant role. This commitment is driving the smart housing trend, positioning New Zealand as a leader in future-focused living.
Understanding Smart Housing
Smart housing refers to homes equipped with advanced automation systems, designed to enhance energy efficiency, security, and overall living conditions. These homes can adapt to the needs of the residents and the environment, using technology to control lighting, heating, and security systems remotely.
- Technology Integration: Smart homes utilize IoT devices and AI to automate home functions.
- Energy Efficiency: Designed to minimize energy consumption and reduce carbon footprint.
- Community Focus: Emphasizes creating a collaborative and sustainable community environment.
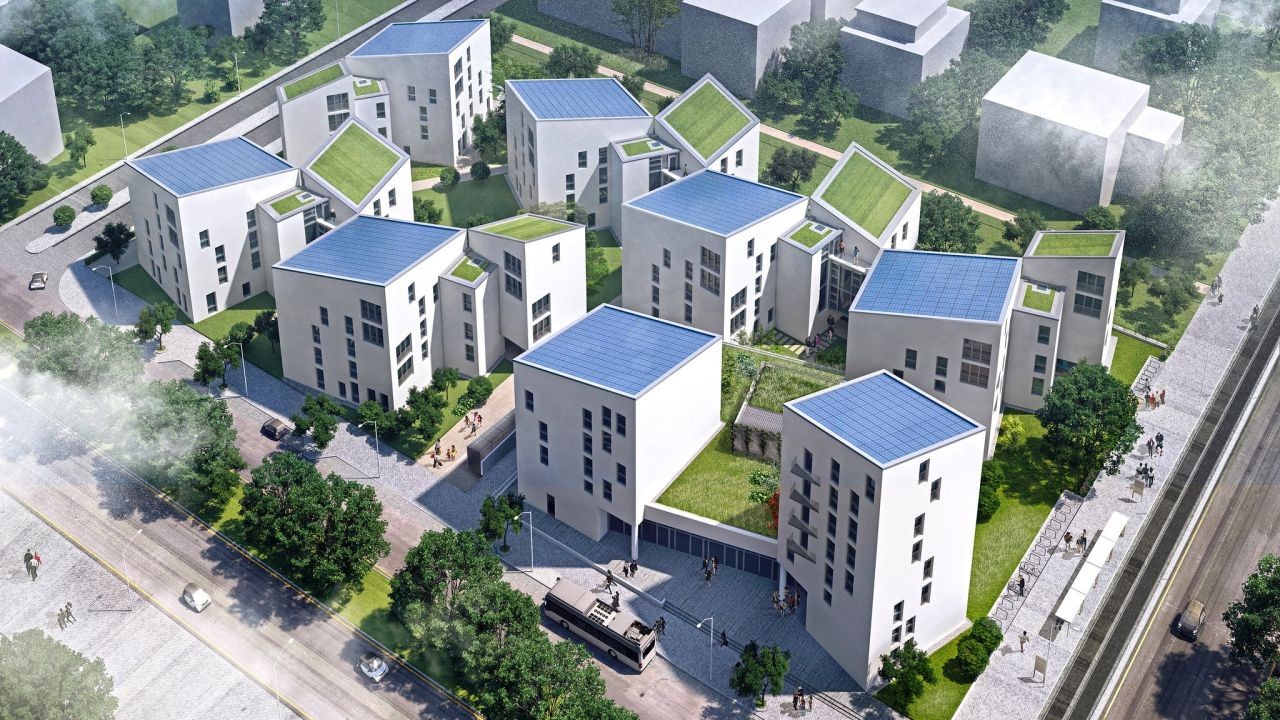
Real-World Case Study: Hobsonville Point
Hobsonville Point, a suburb in Auckland, is a flagship example of smart housing in New Zealand.
- Problem: Auckland faced a housing shortage, with a need for sustainable development.
- Action: The development integrated smart technology and sustainable practices, including solar power and rainwater harvesting systems.
- Result: The community now enjoys reduced energy costs, and a 30% increase in green space, promoting a healthier lifestyle.
- Takeaway: Smart housing developments like Hobsonville Point demonstrate the potential for sustainable urban growth in New Zealand.
Industry Insights and Expert Opinions
Rebecca Harrison, a print media and publishing specialist, emphasizes the importance of integrating technology with sustainable practices. "Smart housing is not just about technology. It’s about creating communities that are resilient and adaptable to future challenges," she states, highlighting the broader impact of these developments.
According to Stats NZ, housing and utilities make up a significant portion of household expenditure. By investing in smart housing, New Zealand can reduce these costs and improve living standards, aligning with the nation's sustainability goals.
Pros vs. Cons of Smart Housing
Pros:
- Higher ROI: Smart homes often have a higher resale value due to their advanced features.
- Sustainability: Reduced energy consumption contributes to environmental conservation.
- Community Benefits: Enhances quality of life through integrated community spaces and services.
Cons:
- High Initial Costs: Upfront investment in technology and infrastructure can be substantial.
- Technological Dependence: Over-reliance on technology may pose challenges if systems fail.
- Privacy Concerns: Increased data collection can lead to privacy issues.
Debunking Myths and Mistakes
Myth vs. Reality
- Myth: Smart homes are only for tech-savvy individuals.
- Reality: These homes are designed to be user-friendly, making them accessible to all age groups.
- Myth: Smart technology increases household energy use.
- Reality: Smart homes actually aim to reduce energy consumption through automation and efficient systems.
Future Trends in Smart Housing
By 2026, smart housing is expected to become more mainstream in New Zealand, driven by policy changes and technological advancements. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand’s focus on sustainable growth supports this trajectory, predicting a 20% increase in smart housing developments over the next five years.
Conclusion
Smart housing developments are not just a trend but a necessity for New Zealand’s future. As these innovations become more prevalent, they promise to address key challenges in the housing sector, from affordability to sustainability. For management consultants and decision-makers, understanding these developments is crucial in shaping future strategies.
What’s Next? To stay ahead in this evolving landscape, engage with local councils and technology providers to explore smart housing solutions. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
People Also Ask
- How does smart housing impact New Zealand? Smart housing can reduce energy costs and improve sustainability, aligning with national goals to reduce carbon emissions.
- What are the biggest misconceptions about smart housing? A common myth is that smart homes are expensive and complicated, but they are designed to be cost-effective and user-friendly.
- Who benefits the most from smart housing? Homeowners, developers, and the environment benefit from smart housing through improved living conditions and sustainability.
Related Search Queries
- Smart housing developments in New Zealand
- Sustainable housing technologies
- IoT in residential properties
- Future of real estate in New Zealand
- Energy-efficient homes
For the full context and strategies on Video Series Exploring New Zealand’s Emerging Smart Housing Developments, see our main guide: Maori Housing Initiatives Community Property Videos Nz.





































my3d figure
4 months ago