Introduction
In the heart of urban Australia, a green revolution is quietly unfolding. As cities expand and the demand for fresh produce climbs, innovative solutions like smart greenhouses and vertical farming emerge as pivotal players in urban agriculture. These cutting-edge technologies promise to redefine traditional farming, offering a sustainable approach to food production amidst the concrete jungles. But what does this mean for the Australian economy, and how can economic development officers harness these trends to drive growth? Let’s delve into the transformative potential of smart greenhouses and vertical farming videos in urban agriculture.
Understanding Smart Greenhouses and Vertical Farming
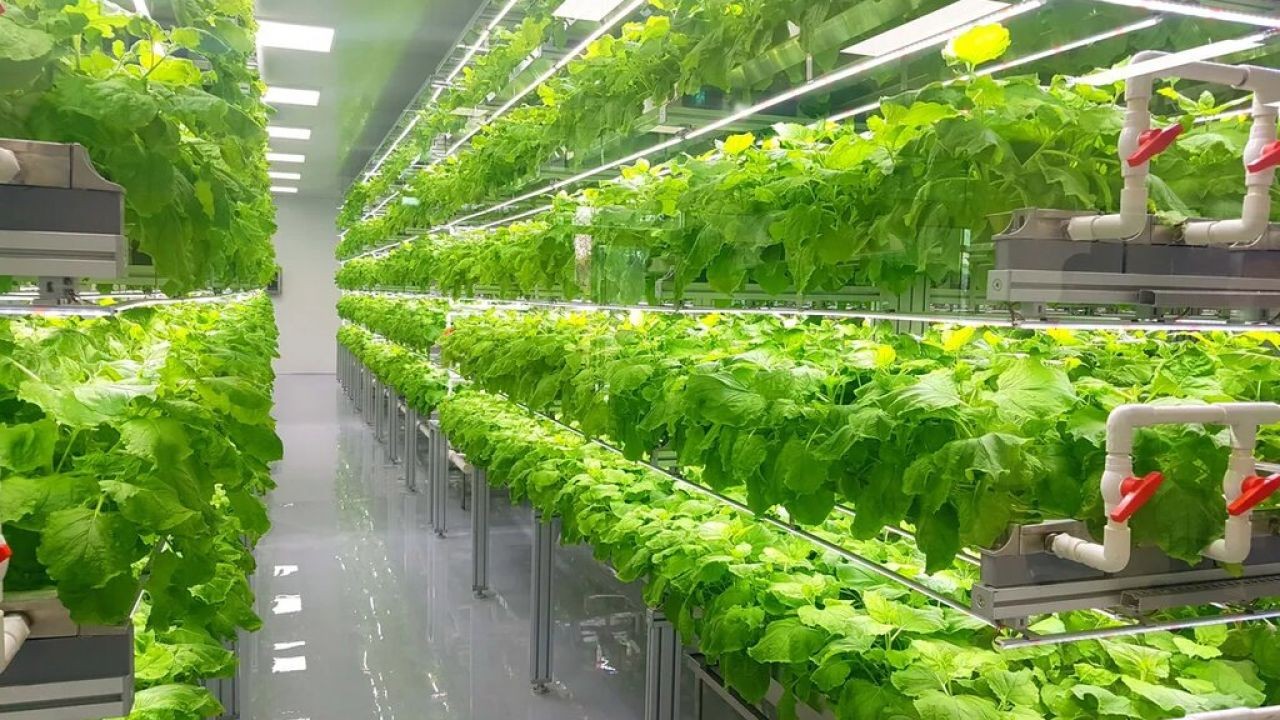
Before diving into actionable strategies, it’s crucial to understand what smart greenhouses and vertical farming entail. Smart greenhouses leverage technology to optimize plant growth, using sensors, automated systems, and data analytics to control environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light. Vertical farming, on the other hand, involves cultivating crops in stacked layers, often integrated into urban buildings, thereby conserving space and resources.
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), agricultural productivity has been a cornerstone of the Australian economy, contributing over AUD 60 billion annually. The integration of smart greenhouse and vertical farming technologies can significantly enhance this sector, offering a sustainable solution to meet the growing demand for fresh produce.
Steps to Implement Smart Greenhouse and Vertical Farming in Urban Areas
1. Conduct a Feasibility Study
Begin by evaluating the viability of smart greenhouses and vertical farming in your urban area. Consider factors such as available space, climate conditions, and local market demand for fresh produce. Collaborate with local universities and research institutions to gather data and insights.
Example: The University of Sydney’s Institute of Agriculture offers resources and expertise that can guide feasibility studies, ensuring projects align with regional agricultural trends and sustainability goals.
2. Secure Funding and Partnerships
Identify potential funding sources, including government grants, private investors, and industry partnerships. The Australian government’s commitment to sustainability and innovation often translates into financial support for green initiatives. Explore opportunities with organizations like the Clean Energy Finance Corporation.
Case Study: In Melbourne, a collaboration between the city council and private investors resulted in a successful vertical farming project that now supplies fresh produce to local supermarkets, reducing transportation costs and emissions.
3. Choose the Right Technology
Select appropriate technologies that suit your specific needs. Smart greenhouses require investment in sensors, automated climate control systems, and data analytics tools. For vertical farming, consider LED lighting, hydroponic systems, and vertical stacking solutions.
Industry Insight: According to a report by Deloitte, integrating AI and IoT in smart greenhouses can increase yield by up to 50%, making it a lucrative investment for urban agriculture projects.
4. Implement Training Programs
Ensure that your team is well-versed in the new technologies. Develop training programs in collaboration with tech providers and agricultural experts to equip staff with the necessary skills for operating and maintaining smart greenhouses and vertical farms.
Example: The Victorian Farmers Federation offers training workshops on sustainable farming practices, including smart technologies, which can be leveraged to enhance workforce capabilities.
5. Monitor and Optimize
Continuous monitoring and optimization are crucial for success. Use data analytics to track plant growth, environmental conditions, and resource use. Adjust systems as needed to maximize efficiency and output.
Data Insight: A study by the CSIRO highlights that real-time monitoring can reduce water usage in smart greenhouses by up to 30%, contributing to resource conservation and cost savings.
Pros and Cons of Smart Greenhouse and Vertical Farming
Pros:
- Increased Yield: Technologies can boost production by optimizing growing conditions.
- Space Efficiency: Vertical farming maximizes urban space, making it ideal for cities.
- Sustainability: Reduces water usage and carbon footprint, aligning with Australia’s environmental goals.
Cons:
- Initial Costs: High upfront investment for technology and infrastructure.
- Technical Complexity: Requires specialized knowledge and training.
- Regulatory Challenges: Navigating zoning laws and compliance can be complex.
Case Study: Sundrop Farms in South Australia
Problem: Sundrop Farms, a pioneer in sustainable agriculture, faced the challenge of producing high-quality tomatoes in arid conditions.
Action: They implemented a cutting-edge greenhouse system powered by solar energy and seawater desalination, integrating advanced technologies to optimize plant growth.
Result: Sundrop Farms now produces over 15,000 tonnes of tomatoes annually, with significantly reduced water usage and carbon emissions, setting a benchmark for sustainable agriculture in Australia.
Takeaway: This case study underscores the potential of smart greenhouses to transform arid regions into productive agricultural hubs, aligning with Australia’s sustainability objectives.
Debunking Common Myths
Myth: "Smart greenhouses are too expensive for small-scale farmers." Reality: While initial costs are high, government incentives and long-term savings on resources can make them financially viable.
Myth: "Vertical farming is only suitable for leafy greens." Reality: Advancements in technology now allow for a broader range of crops, including fruits and herbs.
Future Trends and Predictions
By 2030, smart greenhouses and vertical farming could account for over 20% of Australia’s agricultural production, driven by technological advancements and urbanization trends. As cities continue to grow, these innovations will play a crucial role in ensuring food security and sustainability, aligning with government targets for reducing carbon emissions.
Conclusion
Smart greenhouses and vertical farming present a promising frontier for urban agriculture in Australia. By embracing these innovations, economic development officers can drive sustainable growth and enhance food security. As the demand for fresh produce rises, the integration of technology in agriculture is not just an option but a necessity. What’s your take on the future of urban agriculture in Australia? Share your insights below!
People Also Ask (FAQ)
How does smart greenhouse technology impact urban agriculture in Australia?
Smart greenhouse technology optimizes growing conditions, increasing yield and sustainability. It helps urban farms produce more food with fewer resources, aligning with Australia’s environmental goals.
What are the biggest misconceptions about vertical farming?
A common myth is that vertical farming is only for leafy greens. However, advancements now allow for diverse crops, including fruits and herbs, expanding its potential in urban agriculture.
Related Search Queries
- Smart greenhouse technology in Australia
- Vertical farming benefits and challenges
- Sustainable urban agriculture solutions
- Innovations in Australian agriculture
- Government support for green initiatives in Australia
For the full context and strategies on Smart Greenhouse and Vertical Farming Videos for Urban Agriculture in Australia, see our main guide: Agri Food Marketing Videos Australia.