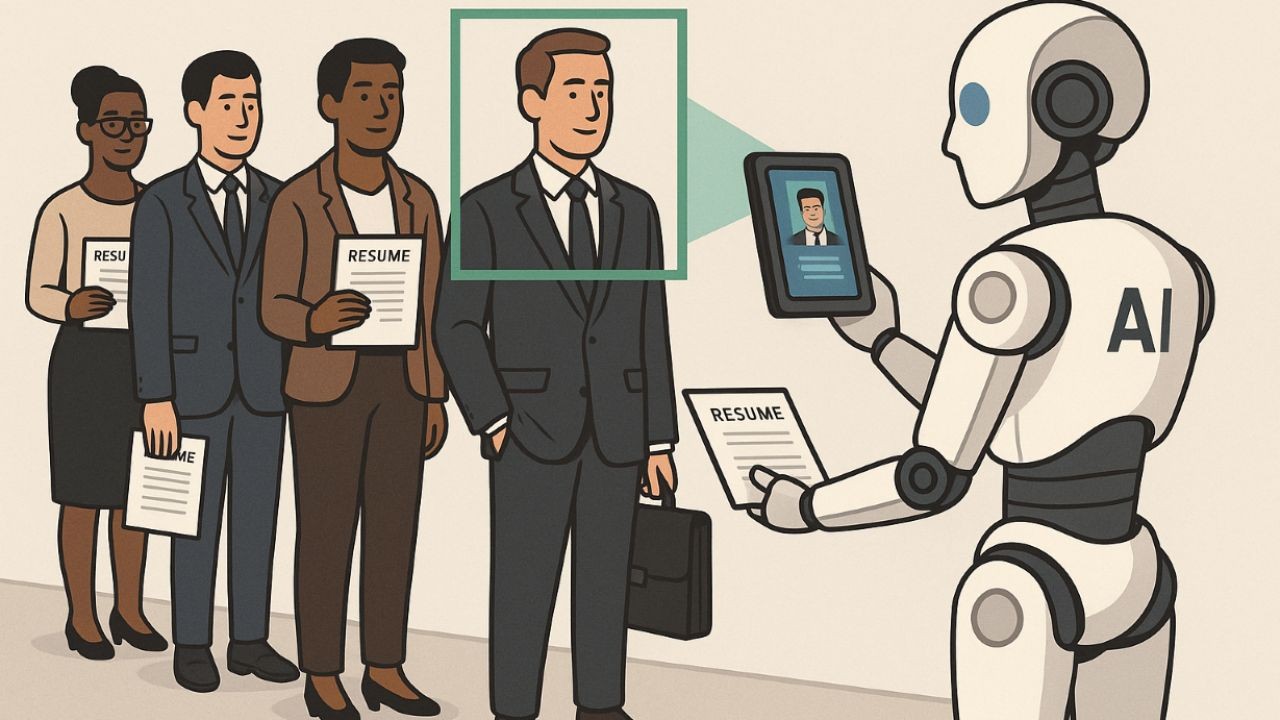
In the rapidly evolving landscape of hiring practices, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as both a boon and a bane. While AI promises efficiency and objectivity, there is a growing concern about its potential biases, especially within the Australian context. The pertinent question arises: Are Australian employers inadvertently discriminating through AI?
A Hidden Opportunity in the Australian Market
Artificial intelligence has rapidly transformed the recruitment landscape in Australia. From resume screening software to automated interview assessment and predictive hiring algorithms, AI promises efficiency, speed, and data-driven objectivity. Yet beneath this veneer of fairness lies a growing concern: AI can reproduce or amplify biases, often without employers realising it.
For Australian businesses, this hidden risk is not just an ethical issue—it also represents a strategic opportunity. Addressing AI bias in hiring can improve workforce diversity, strengthen brand reputation, and unlock untapped talent.
How AI Is Used in Australian Hiring Practices
Australian companies are increasingly relying on AI tools to handle high-volume recruitment, shortlist candidates, and even evaluate cultural fit. These systems analyse resumes, cover letters, social profiles, and video interviews, generating scores or recommendations that influence hiring decisions.
The promise is compelling: AI can reduce administrative workload, increase efficiency, and standardise evaluation criteria. However, the technology is only as objective as the data it is trained on and the assumptions embedded by developers.
The Hidden Bias Problem
Bias in AI hiring systems often emerges unintentionally. Historical recruitment data, societal stereotypes, and incomplete datasets can all influence algorithmic decision-making. For example, if a model is trained on a company’s past hiring patterns that favoured certain schools, genders, or ethnicities, it can inadvertently perpetuate those patterns.
In Australia, where diversity and inclusion are critical workforce priorities, such hidden biases pose real risks. Candidates from minority groups, regional areas, or non-traditional backgrounds may be filtered out despite being fully qualified, creating systemic inequities.
Unseen Impacts on Australian Employers
The consequences of AI bias extend beyond ethics. Australian businesses may face reputational damage, decreased employee morale, and potential legal risk under anti-discrimination laws. Unintended exclusion of qualified candidates also limits access to high-performing talent, particularly in industries experiencing skill shortages, such as technology, healthcare, and engineering.
Moreover, workforce homogeneity can stifle innovation and competitiveness, undermining the very efficiency AI was intended to create.
Regulatory Landscape in Australia
Australia’s Equal Opportunity laws and anti-discrimination frameworks apply to AI-driven recruitment, even if the bias is unintentional. Employers are responsible for ensuring their hiring processes comply with legislation, meaning unchecked algorithms could expose organisations to complaints, audits, or penalties.
The Australian Human Rights Commission has highlighted AI bias as a priority issue, urging businesses to evaluate tools for fairness and transparency. This guidance signals that AI ethics is moving from optional best practice to regulatory expectation.
The Opportunity for Change
Addressing AI bias is not just about mitigation—it is a market opportunity. Australian employers who proactively audit algorithms, diversify training data, and implement human oversight can unlock several advantages.
Companies that reduce bias are likely to attract a broader talent pool, improve retention, and demonstrate social responsibility, enhancing brand perception. Furthermore, integrating fairness into AI recruitment can differentiate businesses in sectors where talent competition is intense.
Practical Steps for Australian Businesses
Mitigating AI bias requires a combination of technological vigilance and organisational awareness. Australian businesses can benefit from measures such as evaluating historical data for skewed patterns, regularly testing AI outputs for discriminatory outcomes, and maintaining human review of automated decisions.
Educating hiring managers and HR teams on algorithmic limitations ensures that AI is a tool for insight, not a substitute for judgment. By adopting a proactive, ethical approach, businesses position themselves to leverage AI effectively while protecting candidate rights and company reputation.
The Future of AI Hiring in Australia
As AI continues to evolve, transparency, explainability, and ethical design will become standard expectations. Australian companies that integrate fairness into recruitment will not only comply with regulations but also benefit from stronger workforce diversity, innovation, and competitive advantage.
Conversely, organisations that ignore bias risk systemic discrimination, legal exposure, and reputational harm—all of which can hinder long-term growth.
Historical Context: The Rise of AI in Hiring
The integration of AI into hiring processes began in the early 2000s, with companies seeking to streamline recruitment. AI tools offered the allure of speed and impartiality, analyzing resumes and screening candidates far quicker than human recruiters. However, as the technology has advanced, so too have the complexities and potential pitfalls associated with its use.
In Australia, the adoption of AI in recruitment accelerated post-2010, driven by a booming tech sector and a competitive job market. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), the national unemployment rate has hovered around 5-6% over the past decade, prompting businesses to refine hiring strategies to secure top talent efficiently.
AI Bias: A Global and Australian Concern
Globally, AI bias has been a topic of intense scrutiny. In the U.S., prominent companies like Amazon faced backlash when their AI recruitment tools favored male candidates for technical roles, leading to the abandonment of the tool. This global concern resonates in Australia, where the Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) has warned against the unchecked use of AI in hiring, highlighting potential biases against women and minorities.
Current Trends and Data-Driven Insights
Recent studies show a concerning trend: AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. In Australia, where the workforce is highly diverse, any inherent bias in AI systems could disproportionately affect minority groups. A report by CSIRO found that AI tools trained on global datasets often fail to account for the unique demographic and cultural nuances present in the Australian workforce.
Moreover, a survey conducted by Australian Human Rights Commission revealed that 35% of respondents believed that AI in recruitment could lead to discrimination, reflecting a significant trust deficit among job seekers.
Case Study: Australian Tech Firm's Approach to AI Bias
Case Study: Atlassian – Eliminating Bias in AI Recruitment
Problem: Atlassian, a prominent Australian software company, discovered that its AI-driven recruitment software was inadvertently biased against women and minority candidates, a common issue recognized globally.
- The company faced a diversity challenge, with underrepresentation of women and minorities in technical roles.
- Internal audits revealed that AI models were trained on historical data that mirrored societal biases.
Action: In response, Atlassian implemented a multifaceted approach to address AI bias.
- They hired a team of AI ethics experts to audit and refine their recruitment algorithms.
- The company integrated diverse data sets into their AI training processes to ensure inclusivity.
Result: Within a year, Atlassian reported significant improvements:
- Female representation in technical roles increased by 15%.
- The overall diversity of new hires rose by 20%, showcasing the effectiveness of their new approach.
Takeaway: Atlassian's proactive measures underscore the importance of continuous evaluation and refinement of AI systems. Australian companies can learn from this case by prioritizing inclusivity in their AI models to enhance diversity.
Pros and Cons of AI in Hiring
Pros:
- Efficiency: AI can quickly process large volumes of applications, reducing the time-to-hire.
- Consistency: Automated systems apply the same criteria to all applicants, potentially reducing human bias.
- Cost-Effective: By streamlining recruitment processes, companies can significantly reduce hiring costs.
Cons:
- Bias Risk: AI systems can perpetuate existing biases if not carefully monitored and adjusted.
- Lack of Transparency: Many AI models operate as "black boxes," making it difficult to understand their decision-making processes.
- Over-reliance: Companies might overlook qualified candidates who do not fit the algorithm's criteria but could excel in the role.
Regulatory Insights and Ethical Considerations
The Australian Human Rights Commission has emphasized the need for businesses to ensure that their AI technologies comply with existing anti-discrimination laws. The commission advises that employers conduct regular audits and impact assessments of their AI tools to identify and mitigate potential biases.
Furthermore, the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) recommends that companies adopt robust governance frameworks to oversee AI usage, emphasizing the importance of accountability and transparency in AI-driven decisions.
Future Trends: The Evolution of AI in Hiring
Looking ahead, the role of AI in recruitment is poised to expand, with increasing sophistication in AI technologies. By 2026, it is predicted that AI will not only streamline the hiring process but also enhance candidate engagement through personalized recruitment experiences.
However, as AI becomes more entrenched in recruitment, Australian businesses must remain vigilant. The integration of ethical AI practices will be crucial in balancing efficiency with fairness. Companies that prioritize transparency and inclusivity will likely gain a competitive edge in attracting diverse talent.
Common Myths & Mistakes
Myth vs. Reality
- Myth: "AI is completely unbiased."
- Reality: AI mirrors the biases present in its training data. A study by University of Sydney found that biased data led to skewed recruitment outcomes, emphasizing the need for diverse data sets.
- Myth: "AI will replace human recruiters."
- Reality: AI is a tool to augment human decision-making, not replace it. According to Deloitte AU, 75% of companies use AI to support, not replace, human judgment in recruitment.
- Myth: "AI systems are self-correcting."
- Reality: Continuous monitoring and updating are required to ensure AI systems remain fair and accurate. An IBM study highlighted the importance of regular AI audits for bias mitigation.
Biggest Mistakes to Avoid
- Avoid assuming AI tools are infallible. Regular audits and updates are essential for maintaining fairness and accuracy.
- Do not neglect the importance of human oversight. Combining AI with human judgment ensures a balanced and thorough recruitment process.
- Relying solely on global data can lead to cultural misalignments. Ensure AI systems are trained with Australian-specific data to reflect local diversity.
People Also Ask
- How does AI impact hiring in Australia? AI enhances efficiency in hiring, but it may also introduce bias if not properly managed. Australian companies report both improved recruitment speed and concern over potential discrimination.
- What are the biggest misconceptions about AI in hiring? A common misconception is that AI is unbiased. However, AI systems can reflect and perpetuate biases present in their training data, requiring careful monitoring.
- What upcoming changes in Australia could affect AI in hiring? By 2026, stricter regulations and guidelines are expected to ensure ethical AI usage in recruitment, emphasizing transparency and accountability.
Conclusion
As AI continues to transform hiring processes, Australian employers must tread carefully to harness its benefits while mitigating its risks. The path forward involves a balanced approach, combining technological advancements with ethical considerations. Employers who prioritize transparency, inclusivity, and continuous improvement will not only comply with regulations but also cultivate a diverse and dynamic workforce.
What strategies have worked for your business in Australia? Share your insights and join the conversation!
Related Search Queries
- AI bias in hiring practices
- Discrimination in Australian workplaces
- AI recruitment tools Australia
- Ethical AI in hiring
- Australian employment laws and AI
- Diversity in Australian tech industry
- AI regulations in Australia
- Future of AI in recruitment
- AI and diversity in hiring
- Impact of AI on Australian job market
For the full context and strategies on AI Bias in Hiring: Are Australian Employers Discriminating Without Knowing? – A Hidden Opportunity in the Australian Market, see our main guide: Australian Creators Made For Australia.