In recent years, New Zealand has witnessed a transformative shift in its building industry, driven by a commitment to sustainability and eco-friendly practices. This movement is not just a trend but a crucial response to the global climate crisis and local environmental challenges. The urgency to adopt sustainable building practices is underscored by New Zealand's ambition to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. This article delves into the rise of eco-friendly building in New Zealand, examining its impact on the economy, the challenges faced, and the future potential of this burgeoning sector.
The Eco-Friendly Building Revolution
The construction industry is one of the largest contributors to carbon emissions globally. In New Zealand, the sector contributes about 20% of the country's greenhouse gas emissions, according to the Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (MBIE). This statistic highlights the pressing need for sustainable practices within the industry. Eco-friendly building, which includes using sustainable materials, energy-efficient designs, and minimizing waste, is increasingly seen as the solution to these environmental challenges.
Pros and Cons of Eco-Friendly Building
The adoption of eco-friendly building practices comes with its set of advantages and challenges.
Pros
- Environmental Impact: Eco-friendly buildings reduce carbon footprints and promote biodiversity. For instance, using local materials minimizes transportation emissions.
- Long-term Cost Savings: Energy-efficient designs reduce utility bills over time, providing financial benefits to homeowners and businesses.
- Increased Property Value: Sustainable buildings often have higher market values and attract environmentally conscious buyers and tenants.
- Health Benefits: These structures improve air quality and natural lighting, enhancing the wellbeing of occupants.
Cons
- Higher Initial Costs: The upfront investment for sustainable materials and technologies can be significant.
- Limited Availability of Materials: Access to eco-friendly materials may be restricted, especially in remote areas.
- Regulatory Challenges: Navigating the regulations for sustainable building can be complex and time-consuming.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: There is a limited number of professionals trained in sustainable building practices.
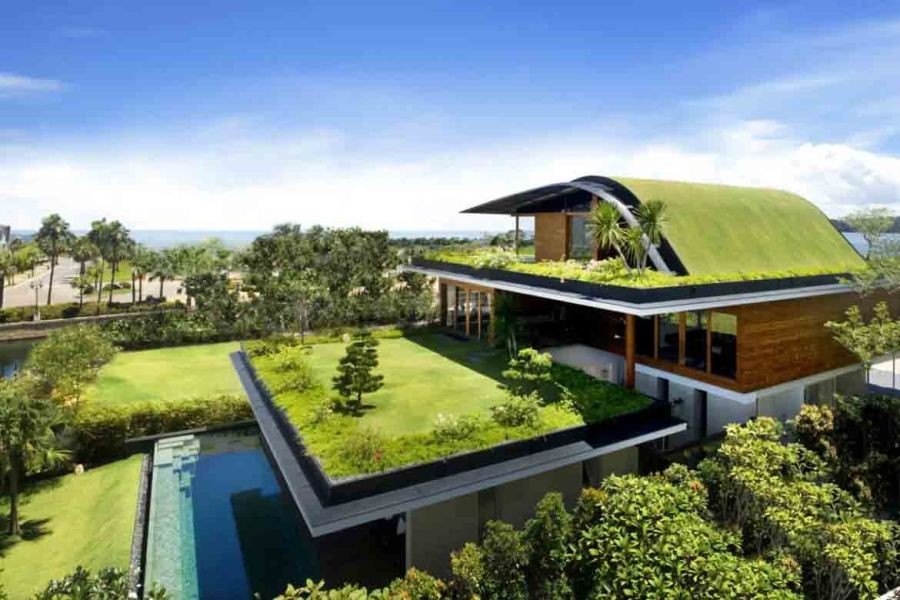
Case Study: Hobsonville Point
Hobsonville Point in Auckland stands as a leading example of sustainable development in New Zealand. This master-planned community integrates eco-friendly practices across its design and construction. The development includes energy-efficient homes, extensive green spaces, and a focus on community engagement.
Problem: The challenge was to create a community that meets the increasing demand for housing while minimizing environmental impact.
Action: The developers implemented a range of sustainability initiatives, including rainwater harvesting systems, solar panels, and native plant landscaping to enhance biodiversity.
Result: Hobsonville Point has become a model for sustainable urban development, with its homes achieving an average 6 Homestar rating—a measure of the health, warmth, and efficiency of New Zealand homes. This has not only increased the market value of properties but also attracted environmentally conscious residents.
Takeaway: This case illustrates the viability and benefits of integrating eco-friendly practices into large-scale developments. It highlights the potential for such projects to contribute positively to both the environment and the economy.
Government Initiatives and Policies
The New Zealand government is actively supporting the transition to sustainable building practices through various initiatives. The introduction of the Building for Climate Change programme by MBIE aims to reduce emissions and improve building resilience. This policy framework sets targets for energy efficiency and encourages the use of low-carbon materials.
Additionally, the government's Green Building Fund provides financial incentives for developers to adopt sustainable practices. According to Stats NZ, these initiatives have led to a 15% increase in the number of green-certified buildings across the country over the past three years.
Challenges and Industry Insights
Despite the progress, the industry faces significant challenges. The cost of sustainable building materials remains a barrier for many developers. According to a report by Deloitte, the initial costs of eco-friendly materials can be 20-30% higher than traditional options. However, industry experts argue that these costs are offset by the long-term savings on energy and maintenance.
Another challenge is the availability of skilled labor. The construction industry in New Zealand is experiencing a skills shortage, particularly in sustainable building practices. To address this, educational institutions are expanding their programs to include sustainability in their curriculum, preparing the next generation of builders and architects.
Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, the future of eco-friendly building in New Zealand is promising. By 2030, it is predicted that sustainable building practices will be mainstream, driven by regulatory requirements and consumer demand. According to a report by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, the green building sector is expected to grow by 8% annually, contributing significantly to the country's GDP.
Emerging technologies such as 3D printing and modular construction are set to revolutionize the industry, making sustainable building more accessible and cost-effective. Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies in buildings will enhance energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The rise of eco-friendly building in New Zealand is not just a response to environmental challenges but a strategic move towards a sustainable future. By embracing these practices, the construction industry can significantly reduce its environmental impact while providing economic benefits. As New Zealand continues to lead in sustainability, businesses and developers are encouraged to innovate and invest in eco-friendly solutions.
Are you ready to be part of this green revolution? Whether you're a homeowner, developer, or policy-maker, there are opportunities to make a difference. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Let's work together towards a sustainable future for New Zealand!
People Also Ask
- How does eco-friendly building impact the New Zealand economy?Eco-friendly building boosts the economy by increasing property values, reducing energy costs, and creating jobs in the sustainable materials sector.
- What are the biggest misconceptions about eco-friendly building?A common myth is that eco-friendly building is too expensive. However, long-term savings on energy and maintenance often outweigh initial costs.
- What upcoming changes in New Zealand could affect eco-friendly building?By 2026, policy updates may mandate stricter energy efficiency standards, influencing the construction landscape significantly.
Related Search Queries
- Eco-friendly building materials NZ
- Sustainable architecture in New Zealand
- Green building certification NZ
- Energy-efficient homes New Zealand
- Future of sustainable building NZ






























jamelktd143064
7 months ago