In the heart of New Zealand, a cultural renaissance is quietly taking shape, driven by a growing recognition of the value in integrating Maori traditions into the nation’s broader cultural practices. This shift is not just a nod to history but a strategic move that could redefine New Zealand’s social and economic landscape. The drive for inclusivity, while culturally enriching, also holds significant implications for industries ranging from tourism to education. "Embracing Maori culture," says Dr. Ella Morgan, a cultural studies expert at the University of Auckland, "offers a unique opportunity for New Zealand to distinguish itself on the global stage, fostering a deeper sense of identity and unity." But what does it mean for a country to weave these traditions into its everyday practices?
Background: The Cultural and Economic Context
New Zealand’s history with the Maori people is complex, marked by periods of both harmony and tension. In recent years, however, there has been a concerted effort to bridge cultural divides. According to Stats NZ, Maori make up about 17% of the population, and their influence is increasingly seen in national policies and cultural events. Economically, this integration is not just a cultural gesture but a potential growth driver. The Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment (MBIE) reported that the tourism sector, which heavily features Maori cultural experiences, contributed approximately NZD 39.1 billion to the economy in 2022, highlighting the financial benefits of cultural inclusivity.
Voices: Experts and Community Leaders Weigh In
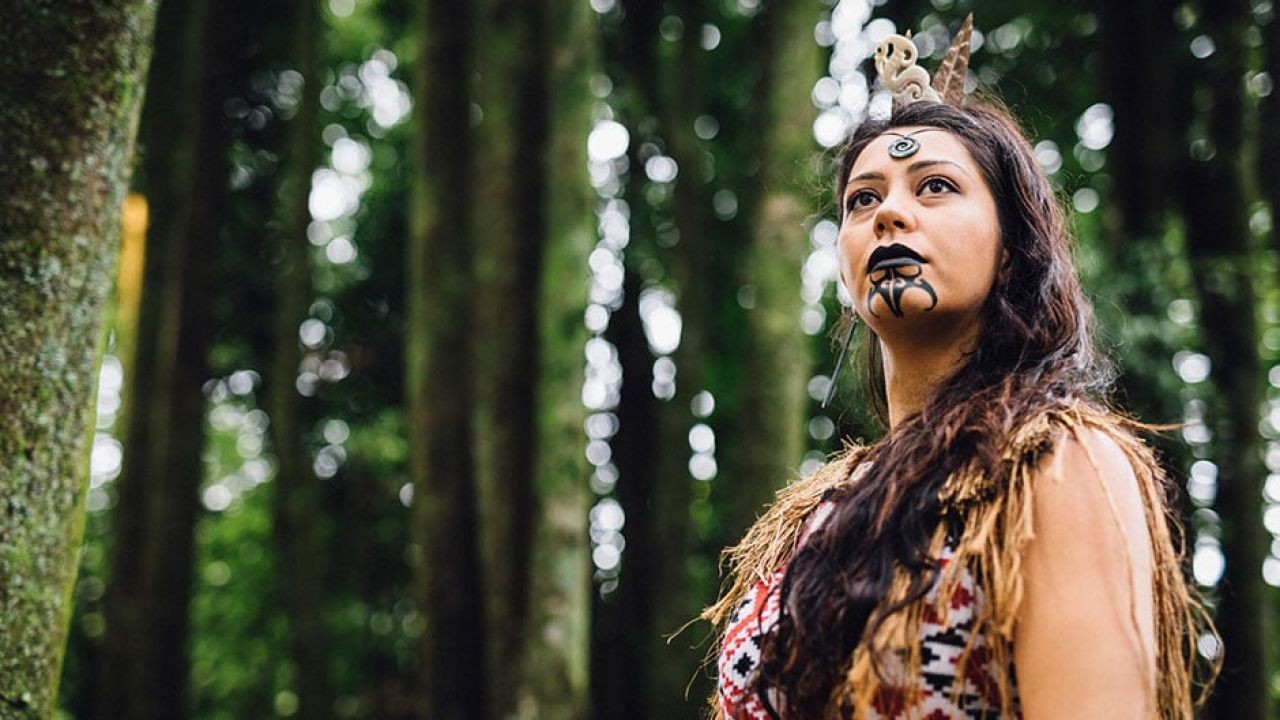
Dr. Morgan is not alone in her assessment. Tame Iti, a respected Maori elder and activist, asserts that "embracing Maori traditions within New Zealand’s cultural fabric is essential for social cohesion." Meanwhile, tourism operators have noted upticks in international interest when Maori cultural elements are prominently featured. "Our guests are looking for authentic experiences," says James Te Whare, owner of a leading eco-tourism business in Rotorua. "Incorporating Maori traditions not only enhances the visitor experience but deepens their connection to New Zealand as a whole."
Case Study: Tourism and Maori Cultural Integration
Case Study: Whakarewarewa – The Living Maori Village
Problem: Whakarewarewa, a Maori cultural site in Rotorua, faced the challenge of declining visitor numbers, which affected the local economy reliant on tourism revenue. The global tourism market was increasingly competitive, with travelers seeking unique cultural encounters.
Action: In response, Whakarewarewa integrated more interactive and educational experiences into their tours, highlighting traditional Maori crafts, rituals, and storytelling. They partnered with local Maori artisans and elders to provide authentic cultural demonstrations and narratives.
Result: Within a year, visitor numbers increased by 30%, and customer satisfaction ratings soared, with many visitors citing the authentic cultural engagement as the highlight of their trip. Revenue from ticket sales and on-site purchases also saw a notable rise.
Takeaway: This case study exemplifies how deeply integrating Maori traditions can enhance the appeal of cultural attractions. For other sectors, adopting similar strategies could not only preserve cultural heritage but also boost economic performance.
Implications: The Broader Impact on New Zealand
The implications of integrating Maori traditions extend beyond tourism. In education, incorporating Te Reo Maori and cultural studies into the curriculum can foster greater understanding and respect among young New Zealanders. This approach aligns with findings from the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, which highlight cultural inclusivity as a factor in improving social outcomes and reducing disparities.
Pros and Cons Analysis
Pros:
- Enhanced Cultural Identity: Strengthens national identity and pride.
- Economic Growth: Increases revenue from tourism and strengthens other industries.
- Social Cohesion: Promotes unity and understanding among diverse populations.
- Global Recognition: Positions New Zealand as a cultural leader.
Cons:
- Implementation Costs: Initial investment in education and training.
- Resistance to Change: Potential pushback from those resistant to change.
- Cultural Misinterpretation: Risks of misrepresentation or commercialization of traditions.
Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, the integration of Maori traditions into New Zealand’s cultural practices is expected to deepen. According to a Deloitte report, cultural tourism is projected to grow by 5% annually, with Maori experiences driving much of this growth. Experts predict that by 2030, Maori cultural elements will be a staple in not just tourism but also in corporate and government sectors, promoting a more inclusive and holistic approach to business and governance.
Common Myths and Mistakes
- Myth: "Maori traditions are only relevant to Maori people." Reality: These traditions are integral to New Zealand’s national identity and offer universal insights into community and environmental stewardship.
- Myth: "Integrating Maori traditions is purely symbolic." Reality: It has tangible economic benefits, as shown by increased tourism revenue and enhanced social outcomes.
- Myth: "There is no interest in Maori culture internationally." Reality: International tourists actively seek authentic cultural experiences, with Maori traditions being a significant draw.
Conclusion
New Zealand stands at the crossroads of cultural preservation and economic opportunity. By embracing Maori traditions, the nation can foster a richer, more inclusive society while simultaneously driving economic growth. The path forward requires commitment and collaboration across sectors, but the rewards are manifold. "It’s about more than economics," says Dr. Morgan. "It’s about preserving a living culture that enriches all who experience it."
What’s your perspective on cultural integration? Share your thoughts and join the conversation!
People Also Ask (FAQ)
- How does integrating Maori traditions impact New Zealand’s economy? Embracing Maori traditions boosts tourism and enhances national identity, contributing significantly to New Zealand's economy.
- What are the challenges of making cultural practices more inclusive? Challenges include overcoming resistance to change and ensuring accurate representation of Maori traditions without commercialization risks.
- What are the best strategies for incorporating Maori traditions into daily practices? Strategies include educational reforms, community engagement, and partnerships with Maori leaders to ensure authenticity and respect.
Related Search Queries
- Maori cultural tourism New Zealand
- New Zealand cultural integration strategies
- Impact of Maori traditions on NZ economy
- Maori cultural practices in education
- Inclusive cultural practices in New Zealand
- Economic benefits of Maori tourism
- Challenges in integrating Maori traditions
- Future of Maori culture in New Zealand
- Maori cultural preservation strategies
- Social cohesion in New Zealand





































muirebarreiro
6 months ago